棕霉素
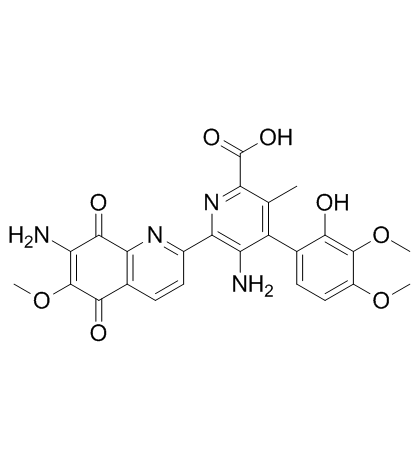
棕霉素结构式

|
常用名 | 棕霉素 | 英文名 | bruneomycin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 3930-19-6 | 分子量 | 506.46400 | |
| 密度 | 1.54g/cm3 | 沸点 | 719ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C25H22N4O8 | 熔点 | 301-303℃ | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 388.7ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS06 |
信号词 | Danger |
棕霉素用途Streptonigrin (Bruneomycin) 是由链霉菌 (Streptomyces flocculus) 产生的一种天然产物,具有抗肿瘤和抗菌活性。Streptonigrin 可作为 pan-PAD 抑制剂,抑制 PAD1,PAD2,PAD3 和 PAD4 的 IC50 分别为 48.3±34.2 μM,26.1±0.3 μM,0.43±0.03 μM 和 2.5±0.4 μM。 |
| 中文名 | 链黑霉素 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | streptonigrin |
| 中文别名 | 棕霉素 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | Streptonigrin (Bruneomycin) 是由链霉菌 (Streptomyces flocculus) 产生的一种天然产物,具有抗肿瘤和抗菌活性。Streptonigrin 可作为 pan-PAD 抑制剂,抑制 PAD1,PAD2,PAD3 和 PAD4 的 IC50 分别为 48.3±34.2 μM,26.1±0.3 μM,0.43±0.03 μM 和 2.5±0.4 μM。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 靶点 |
Anti-bacterial[1] IC50: 48.3±34.2 µM (PAD1), 26.1±0.3 µM, (PAD2), 0.43±0.03 µM (PAD3), 2.5±0.4 µM (PAD4)[1] |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.54g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 719ºC at 760mmHg |
| 熔点 | 301-303℃ |
| 分子式 | C25H22N4O8 |
| 分子量 | 506.46400 |
| 闪点 | 388.7ºC |
| 精确质量 | 506.14400 |
| PSA | 197.18000 |
| LogP | 3.59940 |
| InChIKey | PVYJZLYGTZKPJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COC1=C(N)C(=O)c2nc(-c3nc(C(=O)O)c(C)c(-c4ccc(OC)c(OC)c4O)c3N)ccc2C1=O |
| 折射率 | 1.716 |
| 储存条件 | 2-8°C |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):0.5 2.氢键供体数量:4 3.氢键受体数量:12 4.可旋转化学键数量:5 5.互变异构体数量:645 6.拓扑分子极性表面积:193 7.重原子数量:37 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:1310 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:1 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 符号 |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Danger |
| 危害声明 | H300 |
| 警示性声明 | P264-P301 + P310 |
| 个人防护装备 | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | T+: Very toxic; |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | 28 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | 53-28-36/37/39-45 |
| 危险品运输编码 | UN 3462 6.1/PG 1 |
| WGK德国 | 3 |
| RTECS号 | TJ7350000 |
| 包装等级 | II |
| 危险类别 | 6.1(a) |
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared ... |
|
|
Mining biologically-active molecules for inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH): Identification of phenmedipham and amperozide as FAAH inhibitors
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 6793-6, (2009) The screening of known medicinal agents against new biological targets has been shown to be a valuable approach for revealing new pharmacology of marketed compounds. Recently, carbamate, urea and keto... |
|
|
High-content single-cell drug screening with phosphospecific flow cytometry.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 4 , 132-42, (2008) Drug screening is often limited to cell-free assays involving purified enzymes, but it is arguably best applied against systems that represent disease states or complex physiological cellular networks... |
| Rufocromomycinum |
| Valacidin |
| Rufocromomycine |
| Bruneomycin |
| Streptonigran |
| (4Z)-5-amino-6-(7-amino-6-methoxy-5,8-dioxoquinolin-2-yl)-4-(4,5-dimethoxy-6-oxocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-ylidene)-3-methyl-1H-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid |
| Nigrin |
| Rufocromomicina |
| Rufocromomycin |


