bruneomycin
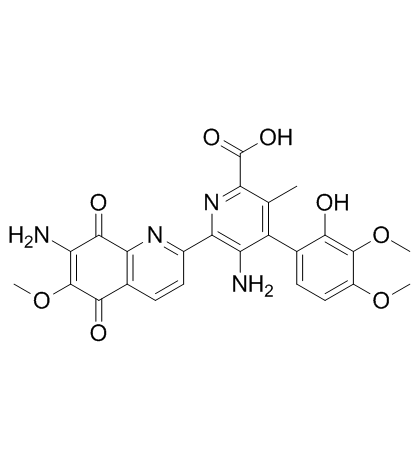
bruneomycin structure
|
Common Name | bruneomycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3930-19-6 | Molecular Weight | 506.46400 | |
| Density | 1.54g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 719ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H22N4O8 | Melting Point | 301-303℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 388.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of bruneomycinStreptonigrin (Bruneomycin), a natural product produced by Streptomyces flocculus, possesses both anti-tumor and anti-bacterial activity. Streptonigrin acts as a pan-PAD inhibitor with IC50s of 48.3±34.2 µM, 26.1±0.3 µM, 0.43±0.03 µM, and 2.5±0.4 µM for PAD1, PAD2, PAD3, and PAD4, respectively[1]. |
| Name | streptonigrin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Streptonigrin (Bruneomycin), a natural product produced by Streptomyces flocculus, possesses both anti-tumor and anti-bacterial activity. Streptonigrin acts as a pan-PAD inhibitor with IC50s of 48.3±34.2 µM, 26.1±0.3 µM, 0.43±0.03 µM, and 2.5±0.4 µM for PAD1, PAD2, PAD3, and PAD4, respectively[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Anti-bacterial[1] IC50: 48.3±34.2 µM (PAD1), 26.1±0.3 µM, (PAD2), 0.43±0.03 µM (PAD3), 2.5±0.4 µM (PAD4)[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.54g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 719ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 301-303℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C25H22N4O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 506.46400 |
| Flash Point | 388.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 506.14400 |
| PSA | 197.18000 |
| LogP | 3.59940 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.716 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300 |
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P301 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+: Very toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | 28 |
| Safety Phrases | 53-28-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 3462 6.1/PG 1 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | TJ7350000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared ... |
|
|
Mining biologically-active molecules for inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH): Identification of phenmedipham and amperozide as FAAH inhibitors
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 6793-6, (2009) The screening of known medicinal agents against new biological targets has been shown to be a valuable approach for revealing new pharmacology of marketed compounds. Recently, carbamate, urea and keto... |
|
|
High-content single-cell drug screening with phosphospecific flow cytometry.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 4 , 132-42, (2008) Drug screening is often limited to cell-free assays involving purified enzymes, but it is arguably best applied against systems that represent disease states or complex physiological cellular networks... |
| Rufocromomycinum |
| Valacidin |
| Rufocromomycine |
| Bruneomycin |
| Streptonigran |
| (4Z)-5-amino-6-(7-amino-6-methoxy-5,8-dioxoquinolin-2-yl)-4-(4,5-dimethoxy-6-oxocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-ylidene)-3-methyl-1H-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid |
| Nigrin |
| Rufocromomicina |
| Rufocromomycin |

