硫酸苯丙胺
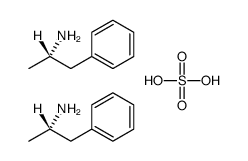
硫酸苯丙胺结构式

|
常用名 | 硫酸苯丙胺 | 英文名 | d-amphetamine sulfate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 51-63-8 | 分子量 | 368.49100 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | 201.5ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C18H28N2O4S | 熔点 | >300° | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 87.4ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS06 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Modulation of locomotor activation by the rostromedial tegmental nucleus.
Neuropsychopharmacology 40(3) , 676-87, (2015) The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg) is a strong inhibitor of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) reported to influence neurobiological and behavioral responses to reward omission, aversive and fear-eliciting stimuli, and certain drugs o... |
|
|
Emotions and motivated behavior converge on an amygdala-like structure in the zebrafish.
Eur. J. Neurosci. 40(9) , 3302-15, (2014) The brain reward circuitry plays a key role in emotional and motivational behaviors, and its dysfunction underlies neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, depression and drug addiction. Here, we characterized the neuronal activity pattern induced by... |
|
|
Effects of withdrawal from an escalating dose schedule of d-amphetamine on sexual behavior in the male rat.
Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 64 , 597, (1999) The present study sought to determine the effect of withdrawal from an escalating dose schedule of d-amphetamine on sexual behavior in male rats. Tests were conducted every 5 days until stable levels of sexual behavior were obtained. With repeated testing, ma... |
|
|
Nucleus accumbens dopamine mediates amphetamine-induced impairment of social bonding in a monogamous rodent species.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107(3) , 1217-22, (2010) The prairie vole (Microtus ochrogaster) is a socially monogamous rodent species that forms pair bonds after mating, a behavior in which central dopamine (DA) has been implicated. Here, we used male prairie voles to examine the effects of drug exposure on pair... |
|
|
The metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor agonists LY354740 and LY379268 selectively attenuate phencyclidine versus d-amphetamine motor behaviors in rats.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 291 , 161, (1999) Previous animal studies have indicated that drugs targeted at metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors may be useful for treatment of psychosis. In this article, the effects of the novel, potent, and selective mGlu2/3 receptor agonists LY354740 and LY379268, a... |
|
|
Amphetamine and extinction of cued fear.
Neurosci. Lett. 468 , 18-22, (2010) Much research is focused on developing novel drugs to improve memory. In particular, psychostimulants have been shown to enhance memory and have a long history of safe use in humans. In prior work, we have shown that very low doses of amphetamine administered... |
|
|
Intrastriatal GDNF gene transfer by inducible lentivirus vectors protects dopaminergic neurons in a rat model of parkinsonism. Chen SS, Yang C, Hao F, et al.
Exp. Neurol. 261 , 87-96, (2014)
|
|
|
d-amphetamine stimulates unconditioned exploration/approach behaviors in crayfish: Towards a conserved evolutionary function of ancestral drug reward
Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 99(1) , 75-80, (2011) In mammals, rewarding properties of drugs depend on their capacity to activate a dopamine-mediated appetitive motivational seeking state—a system that allows animals to pursue and find all kinds of objects and events needed for survival. With such states stro... |