2,3-二甲氧基-1,4-萘醌
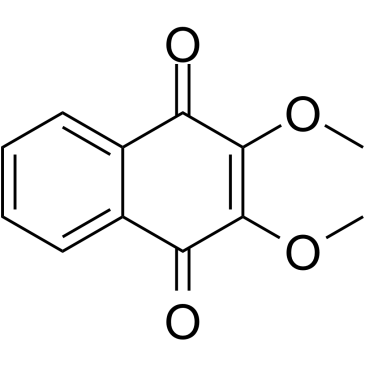
2,3-二甲氧基-1,4-萘醌结构式

|
常用名 | 2,3-二甲氧基-1,4-萘醌 | 英文名 | DMNQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 6956-96-3 | 分子量 | 218.20500 | |
| 密度 | 1.28g/cm3 | 沸点 | 392.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C12H10O4 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 177.6ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Carvacrol and rosemary essential oil manifest cytotoxic, DNA-protective and pro-apoptotic effect having no effect on DNA repair.
Neoplasma 61(6) , 690-9, (2014) For several thousand years natural products were successfully used to treat a variety of diseases and to maintain health in humans, but until now it is not fully known what causes these medicinal effects. In our study we assessed the cytotoxic, DNA-protective... |
|
|
Posttranslational Regulation of Human DNA Polymerase ι.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 27332-44, (2015) Human DNA polymerases (pols) η and ι are Y-family DNA polymerase paralogs that facilitate translesion synthesis past damaged DNA. Both polη and polι can be monoubiquitinated in vivo. Polη has been shown to be ubiquitinated at one primary site. When this site ... |
|
|
Hypoxia drives transient site-specific copy gain and drug-resistant gene expression.
Genes Dev. 29 , 1018-31, (2015) Copy number heterogeneity is a prominent feature within tumors. The molecular basis for this heterogeneity remains poorly characterized. Here, we demonstrate that hypoxia induces transient site-specific copy gains (TSSGs) in primary, nontransformed, and trans... |
|
|
Cancer-associated fibroblasts expressing CXCL14 rely upon NOS1-derived nitric oxide signaling for their tumor-supporting properties.
Cancer Res. 74(11) , 2999-3010, (2014) Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) stimulate tumor growth and metastasis. Signals supporting CAF function are thus emerging as candidate therapeutic targets in the tumor microenvironment. The chemokine CXCL14 is a potent inducer of CAF protumorigenic functio... |
|
|
Quinone-induced protein handling changes: implications for major protein handling systems in quinone-mediated toxicity.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 280(2) , 285-95, (2014) Para-quinones such as 1,4-Benzoquinone (BQ) and menadione (MD) and ortho-quinones including the oxidation products of catecholamines, are derived from xenobiotics as well as endogenous molecules. The effects of quinones on major protein handling systems in ce... |
|
|
Synthesis and evaluation of antitumor activity of novel 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives (IV).
Arch. Pharm. Res. 29(2) , 123-30, (2006) 1,4-Naphthoquinones are widely distributed in nature and many clinically important antitumor drugs containing a quinone moiety, such as anthracyclines, mitoxantrones and saintopin, show excellent anticancer activity. In this study, 2- or 6-substituted 5,8-dim... |
|
|
Dexamethasone enhances oxidative stress-induced cell death in murine neural stem cells.
Neurotox. Res. 22(2) , 127-37, (2012) Glucocorticoids (GCs) are essential for normal brain development; however, there is consistent evidence that prenatal exposure of the fetal brain to excess GCs permanently modifies the phenotype of neuronal cells. In this paper, the murine-derived multipotent... |
|
|
Classification of heavy-metal toxicity by human DNA microarray analysis.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 41(10) , 3769-74, (2007) Microarray technology is proving to be a useful tool to classify undefined environmental toxicants, to investigate underlying mechanisms of toxicity, and to identify candidate toxicant-specific genetic markers by examining global effects of putative toxicants... |
|
|
Oxidative stress induces internalization of the bile salt export pump, Bsep, and bile salt secretory failure in isolated rat hepatocyte couplets: a role for protein kinase C and prevention by protein kinase A.
Toxicol. Sci. 91(1) , 150-8, (2006) We have shown that Ca2+-mediated protein kinase C (PKC) activation induces impairment of bile salt secretory function and F-actin redistribution in hepatocyte couplets. Because oxidative stress induces Ca2+ elevation, we tested here whether PKC inhibition or ... |
|
|
Redox modulation of global phosphatase activity and protein phosphorylation in intact skeletal muscle.
J. Physiol. 587(Pt 23) , 5767-81, (2009) Skeletal muscles produce transient reactive oxygen species (ROS) in response to intense stimulation, disuse atrophy, heat stress, hypoxia, osmotic stress, stretch and cell receptor activation. The physiological significance is not well understood. Protein pho... |