腺苷钴胺
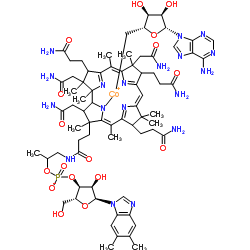
腺苷钴胺结构式

|
常用名 | 腺苷钴胺 | 英文名 | coenzyme B12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 13870-90-1 | 分子量 | 1579.582 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | C72H99CoN18O17P | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | N/A |
|
Thermophilic Coenzyme B12-Dependent Acyl Coenzyme A (CoA) Mutase from Kyrpidia tusciae DSM 2912 Preferentially Catalyzes Isomerization of (R)-3-Hydroxybutyryl-CoA and 2-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81 , 4564-72, (2015) The recent discovery of a coenzyme B12-dependent acyl-coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) mutase isomerizing 3-hydroxybutyryl- and 2-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA in the mesophilic bacterium Aquincola tertiaricarbonis L108 (N. Yaneva, J. Schuster, F. Schäfer, V. Lede, D. Przybylsk... |
|
|
Assessing the stability of membrane proteins to detect ligand binding using differential static light scattering.
J. Biomol. Screen. 15 , 314-20, (2010) Protein stabilization upon ligand binding has frequently been used to identify ligands for soluble proteins. Methods such as differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF) and differential static light scattering (DSLS) have been employed in the 384-well format and ... |
|
|
Chemical screening methods to identify ligands that promote protein stability, protein crystallization, and structure determination.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103 , 15835-40, (2006) The 3D structures of human therapeutic targets are enabling for drug discovery. However, their purification and crystallization remain rate determining. In individual cases, ligands have been used to increase the success rate of protein purification and cryst... |
|
|
Processing of alkylcobalamins in mammalian cells: A role for the MMACHC (cblC) gene product.
Mol. Genet. Metab. 97 , 260-266, (2009) The MMACHC gene product of the cblC complementation group, referred to as the cblC protein, catalyzes the in vitro and in vivo decyanation of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B(12)). We hypothesized that the cblC protein would also catalyze the dealkylation of newly i... |
|
|
Vitamin B12-derivatives-enzyme cofactors and ligands of proteins and nucleic acids.
Chem. Soc. Rev. 40 , 4346-4363, (2011) B(12)-cofactors play important roles in the metabolism of microorganisms, animals and humans. Microorganisms are the only natural sources of B(12)-derivatives, and the latter are "vitamins" for other B(12)-requiring organisms. Some B(12)-dependent enzymes cat... |
|
|
B12 trafficking in mammals: A for coenzyme escort service.
ACS Chem. Biol. 1 , 149-159, (2006) Many coenzymes are vitamins that are assimilated in mammals into their active form from precursors obtained from the diet. They are often both rare and reactive rendering the likelihood low that the cell uses a collision-based strategy for their delivery to d... |
|
|
A human vitamin B12 trafficking protein uses glutathione transferase activity for processing alkylcobalamins.
J. Biol. Chem. 284 , 33418-33424, (2009) Pathways for tailoring and processing vitamins into active cofactor forms exist in mammals that are unable to synthesize these cofactors de novo. A prerequisite for intracellular tailoring of alkylcobalamins entering from the circulation is removal of the alk... |
|
|
Structural basis of multifunctionality in a vitamin B12-processing enzyme.
J. Biol. Chem. 286 , 29780-29787, (2011) An early step in the intracellular processing of vitamin B(12) involves CblC, which exhibits dual reactivity, catalyzing the reductive decyanation of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B(12)), and the dealkylation of alkylcobalamins (e.g. methylcobalamin; MeCbl). Insigh... |
|
|
Adenosyltransferase: an enzyme and an escort for coenzyme B12?
Trends Biochem. Sci. 30 , 304-308, (2005) Many organic cofactors are both rare and reactive. They are usually in low abundance, which poses problems for efficient collision-based targeting to dependent enzymes, whereas their reactivity is problematic for side reactions. Sequestration and escorted del... |
|
|
Role of histidine 225 in adenosylcobalamin-dependent ornithine 4,5-aminomutase.
Bioorg. Chem. 40(1) , 39-47, (2012) Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP), in the active site of ornithine 4,5-aminomutase (OAM), forms a Schiff base with N(δ) of the d-ornithine side chain and facilitates interconversion of the amino acid to (2R, 4S) 2,4-diaminopentanoic acid via a radical-based mechan... |