| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
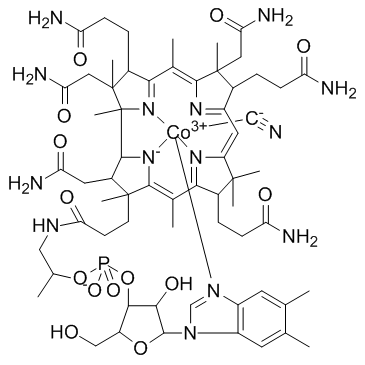 |
维生素b12
CAS:68-19-9 |
|
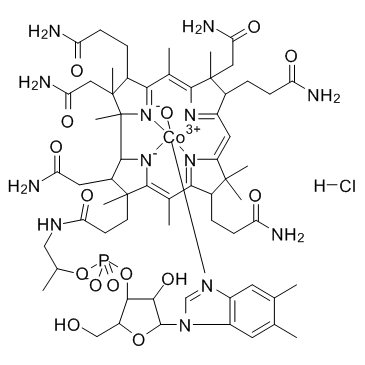 |
维生素 B12A
CAS:59461-30-2 |
|
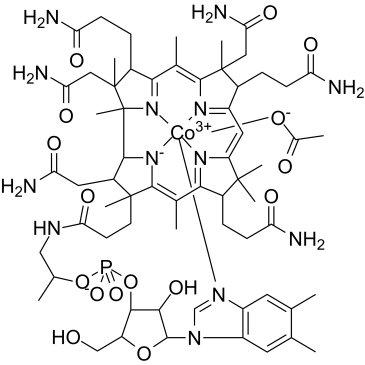 |
羟钴胺素乙酸盐
CAS:22465-48-1 |
|
 |
甲钴胺
CAS:13422-55-4 |
|
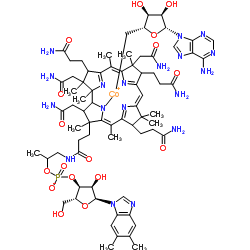 |
腺苷钴胺
CAS:13870-90-1 |