氟哌酸
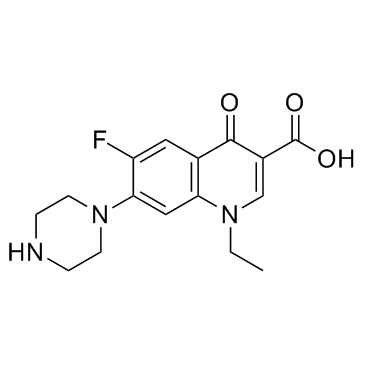
氟哌酸结构式

|
常用名 | 氟哌酸 | 英文名 | Norfloxacin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 70458-96-7 | 分子量 | 319.331 | |
| 密度 | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 555.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C16H18FN3O3 | 熔点 | 220°C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 289.9±30.1 °C |
|
Phenotypic heterogeneity enables uropathogenic Escherichia coli to evade killing by antibiotics and serum complement.
Infect. Immun. 83(3) , 1056-67, (2015) Uropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli (UPEC) are the major cause of bacteremic urinary tract infections. Survival in the bloodstream is associated with different mechanisms that help to resist serum complement-mediated killing. While the phenotypic hetero... |
|
|
Genotypes and oxacillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus from chicken and chicken meat in Poland.
Poult. Sci. 93(12) , 3179-86, (2014) The genotypes and oxacillin resistance of 263 Staphylococcus aureus isolates cultured from chicken cloacae (n = 138) and chicken meat (n = 125) was analyzed. Fifteen spa types were determined in the studied S. aureus population. Among 5 staphylococcal protein... |
|
|
Efflux-related resistance to norfloxacin, dyes, and biocides in bloodstream isolates of Staphylococcus aureus.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 3235-9, (2007) Efflux is an important resistance mechanism in Staphylococcus aureus, but its frequency in patients with bacteremia is unknown. Nonreplicate bloodstream isolates were collected over an 8-month period, and MICs of four common efflux pump substrates, with and w... |
|
|
RamA confers multidrug resistance in Salmonella enterica via increased expression of acrB, which is inhibited by chlorpromazine.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52 , 3604-11, (2008) Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium SL1344, in which efflux pump genes (acrB, acrD, acrF, tolC) or regulatory genes thereof (marA, soxS, ramA) were inactivated, was grown in the presence of 240 antimicrobial and nonantimicrobial agents in the Biolog Pheno... |
|
|
In vitro antibacterial activities of JNJ-Q2, a new broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54 , 1955-64, (2010) JNJ-Q2, a novel fluorinated 4-quinolone, was evaluated for its antibacterial potency by broth and agar microdilution MIC methods in studies focused on skin and respiratory tract pathogens, including strains exhibiting contemporary fluoroquinolone resistance p... |
|
|
Overexpression of patA and patB, which encode ABC transporters, is associated with fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55 , 190-6, (2011) Fifty-seven clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae were divided into four groups based on their susceptibilities to the fluoroquinolones ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin and the dyes ethidium bromide and acriflavine. Comparative reverse transcription-PCR ... |
|
|
Fluoroquinolone efflux by the plasmid-mediated multidrug efflux pump QacB variant QacBIII in Staphylococcus aureus.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54 , 4107-11, (2010) Plasmids that carry the multidrug efflux genes qacA and qacB are widely distributed in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Although the QacA and QacB proteins are similar to each other, their respective substrate specificities may differ. We i... |
|
|
Cloning, nucleotide sequencing, and analysis of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump of Enterobacter cloacae and determination of its involvement in antibiotic resistance in a clinical isolate.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 3247-53, (2007) Enterobacter cloacae is an emerging clinical pathogen that may be responsible for nosocomial infections. Management of these infections is often difficult, owing to the high frequency of strains that are resistant to disinfectants and antimicrobial agents in ... |
|
|
Functional cloning and characterization of the multidrug efflux pumps NorM from Neisseria gonorrhoeae and YdhE from Escherichia coli.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52 , 3052-60, (2008) Active efflux of antimicrobial agents is one of the most important adapted strategies that bacteria use to defend against antimicrobial factors that are present in their environment. The NorM protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and the YdhE protein of Escherichi... |
|
|
New plasmid-mediated fluoroquinolone efflux pump, QepA, found in an Escherichia coli clinical isolate.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 3354-60, (2007) Plasmid-mediated Qnr and AAC(6')-Ib-cr have been recognized as new molecular mechanisms affecting fluoroquinolone (FQ) resistance. C316, an Escherichia coli strain demonstrating resistance to various FQs, was isolated in Japan. Resistance to FQs was augmented... |