依巴斯汀
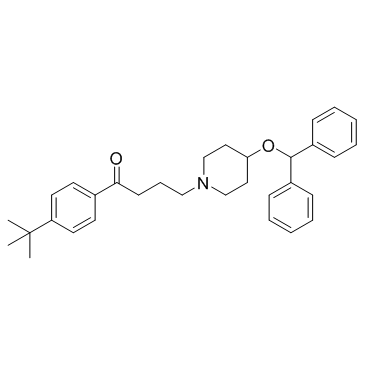
依巴斯汀结构式

|
常用名 | 依巴斯汀 | 英文名 | Ebastine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 90729-43-4 | 分子量 | 469.658 | |
| 密度 | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 596.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C32H39NO2 | 熔点 | 80-82°C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 314.5±30.1 °C |
|
Anaphylaxis to oral iron salts. desensitization protocol for tolerance induction.
J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 18(4) , 305-8, (2008) Allergies to iron salts are seldom reported. We studied a patient with iron-deficiency anemia who had suffered anaphylactic reactions caused by oral iron salts. An allergy study was performed using single-blind, placebo-controlled oral challenge and skin test... |
|
|
A novel approach for predicting P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) inhibition using molecular interaction fields.
J. Med. Chem. 54 , 1740-51, (2011) P-glycoprotein (Pgp or ABCB1) is an ABC transporter protein involved in intestinal absorption, drug metabolism, and brain penetration, and its inhibition can seriously alter a drug's bioavailability and safety. In addition, inhibitors of Pgp can be used to ov... |
|
|
New therapies for allergic rhinitis.
Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 14(4) , 422, (2014) Because of its burden on patient's lives and its impact on asthma, allergic rhinitis must be treated properly with more effective and safer treatments. According to guidelines by Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Asthma (ARIA), the classification, pathogene... |
|
|
Analysis of disease-dependent sedative profiles of H(1)-antihistamines by large-scale surveillance using the visual analog scale.
Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 30(3) , 225-30, (2008) Sedation is the most frequent side effect of H(1)-antihistamines, and, sometimes, it may be life-threatening for patients. Evaluation of the sedative properties of H(1)-antihistamines is important to improve the patients' quality of life (QOL). Therefore, we ... |
|
|
Acquired cold urticaria symptoms can be safely prevented by ebastine.
Allergy 62(12) , 1465-8, (2007) Acquired cold urticaria (ACU) is a skin condition, in which exposure to cold results in wheals and itching and sometimes general systemic complications. It has a profound impact on patient quality of life. Second-generation antihistamines are recommended as t... |
|
|
Clinical characteristics and therapeutic outcomes of patients with localized mucosal allergy.
Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 24(4) , e89-92, (2010) Many researchers have focused on the definition and pathophysiology of localized mucosal allergy. However, there are few studies on its clinical characteristics and therapeutic outcomes. The goal of this study was to analyze the prevalence, epidemiology, clin... |
|
|
A high-content biosensor-based screen identifies cell-permeable activators and inhibitors of EGFR function: implications in drug discovery.
J. Biomol. Screen. 17(7) , 885-99, (2012) Early success of kinase inhibitors has validated their use as drugs. However, discovery efforts have also suffered from high attrition rates due to lack of cellular activity. We reasoned that screening for such candidates in live cells would identify novel ce... |
|
|
Preseasonal prophylactic treatment with antihistamines suppresses IL-5 but not IL-33 mRNA expression in the nasal mucosa of patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis caused by Japanese cedar pollen.
Acta Otolaryngol. 132(4) , 434-8, (2012) These findings suggest that the down-regulation of interleukin (IL)-5 gene expression in collaboration with the suppression of histamine H(1) receptor (H1R) gene expression in the nasal mucosa provides the basis for better therapeutic effects of preseasonal p... |
|
|
Implementation of guidelines for allergic rhinitis in specialist practices. A randomized pragmatic controlled trial.
Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 150(1) , 75-82, (2009) Guidelines for allergic rhinitis are more effective than free-treatment choice in the control of seasonal allergic rhinitis.To validate the ARIA (Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma) guidelines in the treatment of intermittent and persistent allergic r... |
|
|
Histamine H(1) antagonist treatment with pyrilamine reduces nicotine self-administration in rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 650(1) , 256-60, (2011) Nicotine has been definitively shown to be critically involved in the neural bases of tobacco addiction. However, nicotine releases a wide variety of neurotransmitters. Nicotine-induced dopamine release has been shown to play a key role in facilitating nicoti... |