| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
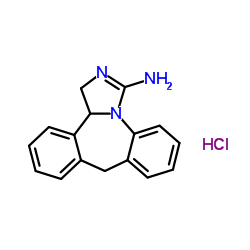 |
盐酸依匹斯汀
CAS:108929-04-0 |
|
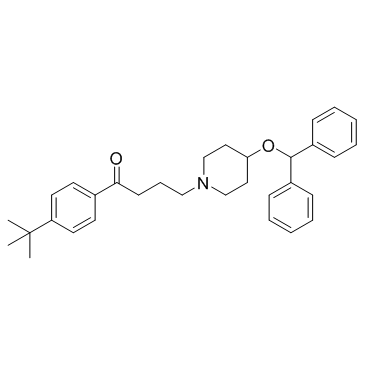 |
依巴斯汀
CAS:90729-43-4 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
盐酸依匹斯汀
CAS:108929-04-0 |
|
 |
依巴斯汀
CAS:90729-43-4 |