D-精氨酸
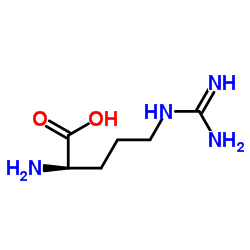
D-精氨酸结构式

|
常用名 | D-精氨酸 | 英文名 | H-D-Arg-OH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 157-06-2 | 分子量 | 174.201 | |
| 密度 | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 367.6±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C6H14N4O2 | 熔点 | 221-224ºC | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 176.1±30.7 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Cloning a neutral protease of Clostridium histolyticum, determining its substrate specificity, and designing a specific substrate.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99 , 10489-99, (2015) Islet transplantation is a prospective treatment for restoring normoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. Islet isolation from pancreases by decomposition with proteolytic enzymes is necessary for transplantation. Two collagenases, collagenase class I (C... |
|
|
Arginase promotes skeletal muscle arteriolar endothelial dysfunction in diabetic rats.
Front. Immunol. 4 , 119, (2013) Endothelial dysfunction is a characteristic feature in diabetes that contributes to the development of vascular disease. Recently, arginase has been implicated in triggering endothelial dysfunction in diabetic patients and animals by competing with endothelia... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of 18 D-amino acids in rat plasma by an ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method: application to explore the potential relationship between Alzheimer's disease and D-amino acid level alterations.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 408 , 141-50, (2016) D-Amino acids are increasingly being recognized as important signaling molecules, and abnormal levels of D-amino acids have been implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. To evaluate the potential relationship between Alzheimer's disease and D-am... |
|
|
Arginine metabolism by macrophages promotes cardiac and muscle fibrosis in mdx muscular dystrophy.
PLoS ONE 5 , e10763, (2010) Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common, lethal disease of childhood. One of 3500 new-born males suffers from this universally-lethal disease. Other than the use of corticosteroids, little is available to affect the relentless progress of the dis... |
|
|
Factors affecting trypanosome maturation in tsetse flies.
PLoS ONE 2 , e239, (2007) Trypanosoma brucei brucei infections which establish successfully in the tsetse fly midgut may subsequently mature into mammalian infective trypanosomes in the salivary glands. This maturation is not automatic and the control of these events is complex. Utili... |
|
|
Purification, properties and alternate substrate specificities of arginase from two different sources: Vigna catjang cotyledon and buffalo liver.
Int. J. Biol. Sci. 1 , 114-22, (2005) Arginase was purified from Vigna catjang cotyledons and buffalo liver by chromatographic separations using Bio-Gel P-150, DEAE-cellulose and arginine AH Sepharose 4B affinity columns. The native molecular weight of an enzyme estimated on Bio-Gel P-300 column ... |
|
|
Role of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in regulating retinal blood flow during flicker-induced hyperemia in cats.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 56 , 3113-20, (2015) To investigate how neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) contributes to regulation of the retinal circulation during rest and flicker stimulation in cats.Using laser Doppler velocimetry, we measured the vessel diameter and blood velocity simultaneously and ca... |
|
|
Novel Route for Agmatine Catabolism in Aspergillus niger Involves 4-Guanidinobutyrase.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81 , 5593-603, (2015) Agmatine, a significant polyamine in bacteria and plants, mostly arises from the decarboxylation of arginine. The functional importance of agmatine in fungi is poorly understood. The metabolism of agmatine and related guanidinium group-containing compounds in... |
|
|
Nitric oxide primes pancreatic beta cells for Fas-mediated destruction in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
J. Exp. Med. 186 , 1193-200, (1997) Fas is an apoptosis-inducing surface receptor involved in controlling tissue homeostasis and function at multiple sites. Here we show that beta cells from the pancreata of newly diagnosed insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) patients express Fas and sho... |
|
|
Nitric oxide signaling mediates stimulation of L-type Ca2+ current elicited by withdrawal of acetylcholine in cat atrial myocytes.
J. Gen. Physiol. 111 , 113-25, (1998) A perforated-patch whole-cell recording method was used to determine whether nitric oxide signaling participates in acetylcholine (ACh)-induced regulation of basal L-type Ca2+ current (ICa,L) in cat atrial myocytes. Exposure to 1 microM ACh for 2 min inhibite... |