3-氰基-N-(1,3-二苯基吡唑-5-基)苯甲酰胺
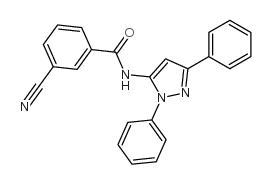
3-氰基-N-(1,3-二苯基吡唑-5-基)苯甲酰胺结构式

|
常用名 | 3-氰基-N-(1,3-二苯基吡唑-5-基)苯甲酰胺 | 英文名 | CDPPB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 781652-57-1 | 分子量 | 364.39900 | |
| 密度 | 1.203g/cm3 | 沸点 | 523.277ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C23H16N4O | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 270.268ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Enhancement of extinction learning attenuates ethanol-seeking behavior and alters plasticity in the prefrontal cortex.
J. Neurosci. 34(22) , 7562-74, (2014) Addiction is a chronic relapsing disorder in which relapse is often initiated by exposure to drug-related cues. The present study examined the effects of mGluR5 activation on extinction of ethanol-cue-maintained responding, relapse-like behavior, and neuronal... |
|
|
The mGluR5 positive allosteric modulator, CDPPB, ameliorates pathology and phenotypic signs of a mouse model of Huntington's disease.
Neurobiol. Dis. 73 , 163-73, (2014) Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal-dominant neurodegenerative disorder caused by a polyglutamine expansion in the amino-terminal region of the huntingtin protein (htt), leading to motor dysfunction, cognitive decline, psychiatric alterations, and death... |
|
|
Therapeutic effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 positive allosteric modulator CDPPB on phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice.
Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 27(5) , 483-8, (2013) This study was undertaken to examine the effects of CDPPB (3-cyano-N-(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)benzamide), a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGlu₅), on cognitive deficits in mice after repeated administration of t... |
|
|
mGlu₅-GABAB interplay in animal models of positive, negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia.
Neurochem. Int. 88 , 97-109, (2015) Diverse preclinical studies exploiting the modulation of the GABAergic and/or glutamatergic system in brain via metabotropic receptors suggest their potential therapeutic utility. GS39783 and CDPPB, positive allosteric modulators of GABAB and mGlu5 receptors,... |
|
|
Dose-dependent effect of CDPPB, the mGluR5 positive allosteric modulator, on recognition memory is associated with GluR1 and CREB phosphorylation in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus
Neuropharmacology 57(5-6) , 531-8, (2009) In the search for strategies to treat schizophrenia, attention has focused on enhancing NMDA receptor function. In vitro experiments show that metabotropic glutamate 5 receptor (mGluR5) activation enhances NMDA receptor activity, and in vivo experiments indic... |
|
|
Mutations causing syndromic autism define an axis of synaptic pathophysiology.
Nature 480 , 63-8, (2011) Tuberous sclerosis complex and fragile X syndrome are genetic diseases characterized by intellectual disability and autism. Because both syndromes are caused by mutations in genes that regulate protein synthesis in neurons, it has been hypothesized that exces... |
|
|
Stress hormone exposure reduces mGluR5 expression in the nucleus accumbens: functional implications for interoceptive sensitivity to alcohol.
Neuropsychopharmacology 39(10) , 2376-86, (2014) Escalations in alcohol drinking associated with experiencing stressful life events and chronic life stressors may be related to altered sensitivity to the interoceptive/subjective effects of alcohol. Indeed, through the use of drug discrimination methods, rat... |
|
|
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 positive allosteric modulators are neuroprotective in a mouse model of Huntington's disease.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 169 , 909-21, (2013) Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder caused by a polyglutamine expansion in the huntingtin protein. We have previously demonstrated that the cell signalling of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) is altered ... |