1α,25-二羟维生素 D2
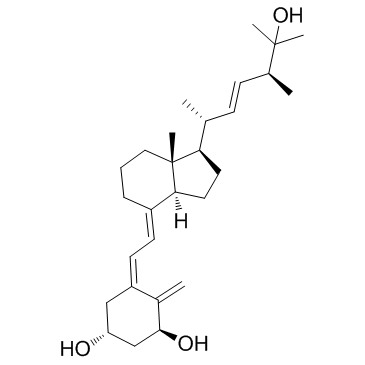
1α,25-二羟维生素 D2结构式

|
常用名 | 1α,25-二羟维生素 D2 | 英文名 | 1-α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 60133-18-8 | 分子量 | 428.647 | |
| 密度 | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 577.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C28H44O3 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 242.5±24.7 °C | |
| 符号 |


GHS02, GHS07 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
5-lipoxygenase is a direct target of miR-19a-3p and miR-125b-5p.
J. Immunol. 194(4) , 1646-53, (2015) 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) is the key enzyme in leukotriene biosynthesis. Leukotrienes are mediators of the innate immune system and inflammatory processes, and they might also be involved in cancer development. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are important translational regul... |
|
|
miR-145 mediates the antiproliferative and gene regulatory effects of vitamin D3 by directly targeting E2F3 in gastric cancer cells.
Oncotarget 6 , 7675-85, (2015) VitaminD3 signaling is involved in inhibiting the development and progression of gastric cancer (GC), while the active vitamin D metabolite 1-alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3)-mediated gene regulatory mechanisms in GC remain unclear. We found that mi... |
|
|
Hologram QSAR model for the prediction of human oral bioavailability.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 , 7738-45, (2007) A drug intended for use in humans should have an ideal balance of pharmacokinetics and safety, as well as potency and selectivity. Unfavorable pharmacokinetics can negatively affect the clinical development of many otherwise promising drug candidates. A varie... |
|
|
Vitamin D and estrogen synergy in Vdr-expressing CD4(+) T cells is essential to induce Helios(+)FoxP3(+) T cells and prevent autoimmune demyelinating disease.
J. Neuroimmunol. 286 , 48-58, (2015) Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurodegenerative disease resulting from an autoimmune attack on the axon-myelin unit. A female MS bias becomes evident after puberty and female incidence has tripled in the last half-century, implicating a female sex hormone inte... |
|
|
Cutting Edge: AhR Is a Molecular Target of Calcitriol in Human T Cells.
J. Immunol. 195 , 2520-3, (2015) The immunoregulatory functions of vitamin D have been well documented in various immunological disorders, including multiple sclerosis, arthritis, and asthma. IL-10 is considered a chief effector molecule that promotes the vitamin D-induced immunosuppressive ... |
|
|
Suppression of murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis development by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 with autophagy modulation.
J. Neuroimmunol. 280 , 1-7, (2015) Multiple sclerosis (MS) has been associated with a history of sub-optimal exposure to ultraviolet light, implicating vitamin D3 as a possible protective agent. We evaluated whether 1,25(OH)2D3 attenuates the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomye... |
|
|
Antiproliferative Activity and in Vivo Toxicity of Double-Point Modified Analogs of 1,25-Dihydroxyergocalciferol.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 24873-94, (2015) Analogs of 1,25-dihydroxyergocalciferol, modified in the side-chain and in the A-ring, were tested for their antiproliferative activity against a series of human cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo toxicity. The proliferation inhibition caused by the analo... |
|
|
The active form of vitamin D, calcitriol, induces a complex dual upregulation of endothelin and nitric oxide in cultured endothelial cells.
Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 307(12) , E1085-96, (2014) Despite the presence of vitamin D receptor (VDR) in endothelial cells, the effect of vitamin D on endothelial function is unknown. An unbalanced production of vasoactive endothelial factors such as nitric oxide (NO) or endothelin-1 (ET-1) results in endotheli... |