邻氨基偶氮甲苯
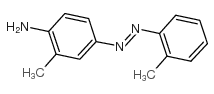
邻氨基偶氮甲苯结构式

|
常用名 | 邻氨基偶氮甲苯 | 英文名 | o-aminoazotoluene |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 97-56-3 | 分子量 | 225.28900 | |
| 密度 | 1.09 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 407.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C14H15N3 | 熔点 | 101-102 °C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 200.4ºC | |
| 符号 |


GHS07, GHS08 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
The calcium-sensing receptor mediates bone turnover induced by dietary calcium and parathyroid hormone in neonates.
J. Bone Miner Res. 26 , 1057-71, (2011) We have investigated, in neonates, whether the calcium-sensing receptor (CaR) mediates the effects of dietary calcium on bone turnover and/or modulates parathyroid hormone (PTH)-induced bone turnover. Wild-type (WT) pups and pups with targeted deletion of the... |
|
|
Endogenous PTH deficiency impairs fracture healing and impedes the fracture-healing efficacy of exogenous PTH(1-34).
PLoS ONE 6(7) , e23060, (2011) Although the capacity of exogenous PTH1-34 to enhance the rate of bone repair is well established in animal models, our understanding of the mechanism(s) whereby PTH induces an anabolic response during skeletal repair remains limited. Furthermore it is unknow... |
|
|
The involvement of a Nanog, Klf4 and c-Myc transcriptional circuitry in the intertwining between neoplastic progression and reprogramming.
Cell Cycle 12(2) , 353-64, (2013) One undisputed milestone of traditional oncology is neoplastic progression, which consists of a progressive selection of dedifferentiated cells driven by a chance sequence of genetic mutations. Recently it has been demonstrated that the overexpression of well... |
|
|
o-Aminoazotoluene does induce the enzymes of its own mutagenic activation in mouse liver.
Toxicology 211(1-2) , 132-8, (2005) The objective of this study was to investigate the CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 mRNAs and enzyme activities in mouse liver during induction with o-aminoazotoluene (OAT) as well as the capability of the hepatic S9-fraction from OAT-treated mice to induce its own activati... |
|
|
Lack of effect of furfural on unscheduled DNA synthesis in the in vivo rat and mouse hepatocyte DNA repair assays and in precision-cut human liver slices.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 39(10) , 999-1011, (2001) The ability of furfural to induce unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) in hepatocytes of male and female B6C3F(1) mice and male F344 rats after in vivo administration and in vitro in precision-cut human liver slices has been studied. Preliminary toxicity studies e... |
|
|
Species-specific effects of the hepatocarcinogens 3'-methyl-4-dimethyl-aminoazobenzene and ortho-aminoazotoluene in mouse and rat liver.
Mol. Carcinog. 44(4) , 223-32, (2005) The effects of rat-specific hepatocarcinogen 3'-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene (3'-MeDAB), mouse-specific hepatocarcinogen ortho-aminoazotoluene (OAT), non-species-specific hepatocarcinogen diethylnitrosamine (DENA), and non-carcinogenic 4'-methyl-4-dimethy... |
|
|
Effects of o-aminoazotoluene on liver regeneration and p53 activation in mice susceptible and resistant to hepatocarcinogenesis.
Toxicology 254(1-2) , 91-6, (2008) The susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) varies greatly within human populations in response to environmental risk agents. The mechanisms underlying differential susceptibility are still largely unknown and need to be clarified to improve HCC chem... |
|
|
Ortho-aminoazotoluene activates mouse constitutive androstane receptor (mCAR) and increases expression of mCAR target genes.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 255(1) , 76-85, (2011) 2'-3-dimethyl-4-aminoazobenzene (ortho-aminoazotoluene, OAT) is an azo dye and a rodent carcinogen that has been evaluated by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as a possible (class 2B) human carcinogen. Its mechanism of action remains unc... |
|
|
Detection of target genes of FOXA transcription factors involved in proliferation control.
Biochemistry. (Mosc.) 73(1) , 70-5, (2008) To reveal the mechanism of tumor-suppressing activity of FOXA proteins in liver, a search for potential target genes of these transcription factors involved in proliferation control was carried out. In the first step, we have used data from the literature con... |
|
|
Promoting effect of o-aminoazotoluene on hepatocarcinogenesis is accompanied by the increase in inflammatory and proliferative processes in liver tissue and decrease in the concentration of free thyroxin in the blood.
Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 144(6) , 821-4, (2007) o-Aminoazotoluene in noncarcinogenic doses promoted the development of liver tumors in female ICR mice induced by administration of diethylnitrosamine during early ontogeny. Severe inflammatory infiltration and proliferation of oval cells were found in liver ... |