4-(3-膦酰基丙基)哌嗪-2-羧酸
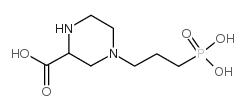
4-(3-膦酰基丙基)哌嗪-2-羧酸结构式

|
常用名 | 4-(3-膦酰基丙基)哌嗪-2-羧酸 | 英文名 | (+/-)-2-HYDROXYTRIDECANOICACID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 100828-16-8 | 分子量 | 252.20 | |
| 密度 | 1.408g/cm3 | 沸点 | 546.7ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C8H17N2O5P | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 284.4ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
High-content screening imaging and real-time cellular impedance monitoring for the assessment of chemical's bio-activation with regards hepatotoxicity.
Toxicol. In Vitro 29 , 1916-31, (2015) Testing hepatotoxicity is a crucial step in the development and toxicological assessment of drugs and chemicals. Bio-activation can lead to the formation of metabolites which may present toxicity for the organism. Classical cytotoxic tests are not always appr... |
|
|
Higher vulnerability and stress sensitivity of neuronal precursor cells carrying an alpha-synuclein gene triplication.
PLoS ONE 9(11) , e112413, (2014) Parkinson disease (PD) is a multi-factorial neurodegenerative disorder with loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and characteristic intracellular inclusions, called Lewy bodies. Genetic predisposition, such as point mutations and copy number v... |
|
|
Regulation of AMPA receptor phosphorylation by the neuropeptide PACAP38.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , 6712-7, (2015) Dynamic changes in synaptic strength are thought to be critical for higher brain function such as learning and memory. Alterations in synaptic strength can result from modulation of AMPA receptor (AMPAR) function and trafficking to synaptic sites. The phospho... |
|
|
Resistance to daunorubicin, imatinib, or nilotinib depends on expression levels of ABCB1 and ABCG2 in human leukemia cells.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 219 , 203-10, (2014) The effect of ABCB1 (P-gp, (P-glycoprotein), MDR1) and ABCG2 (BCRP1, (breast cancer resistance protein 1)) expressions on cell resistance to daunorubicin (DRN), imatinib, and nilotinib was studied in human leukemia cells. We used a set of cells derived from a... |
|
|
Antigen receptor-mediated depletion of FOXP3 in induced regulatory T-lymphocytes via PTPN2 and FOXO1.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 8576, (2016) Regulatory T-cells induced via IL-2 and TGFβ in vitro (iTreg) suppress immune cells and are potential therapeutics during autoimmunity. However, several reports described their re-differentiation into pathogenic cells in vivo and loss of their key functional ... |
|
|
Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells Differentiate into Oligodendrocyte Progenitors Using the Expression of Olig2 Transcription Factor.
Cells Tissues Organs 200 , 93-103, (2015) The helix-loop-helix transcription factor Olig2 is essential for lineage determination of oligodendrocytes. Differentiation of stem cells into oligodendrocytes and transplanting them is a novel strategy for the repair of different demyelination diseases. Dent... |
|
|
Validation of cyclooxygenase-2 as a direct anti-inflammatory target of 4-O-methylhonokiol in zymosan-induced animal models.
Arch. Pharm. Res. 38 , 813-25, (2015) 4-O-methylhonokiol (MH) is known to inhibit inflammation by partially understood mechanisms. Here, the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of MH were examined using enzymatic, cellular, and animal assays. In enzymatic assays, MH inhibited COX-2 activity with an IC50... |
|
|
Upregulation of Runt-Related Transcription Factor-2 Through CCAAT Enhancer Binding Protein-β Signaling Pathway in Microglial BV-2 Cells Exposed to ATP.
J. Cell Physiol. 230 , 2510-21, (2015) We have shown constitutive expression of the master regulator of osteoblastogenesis, runt-related transcription factor-2 (Runx2), by microglia cells outside bone. Here, we attempted to evaluate the pathological significance of Runx2 in microglial BV-2 cells e... |
|
|
Identification of AP80978, a novel small-molecule inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication that targets NS4B.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(6) , 3399-410, (2014) A small-molecule inhibitor of hepatitis C virus (HCV) designated AP89652 was identified by screening a compound library with an HCV genotype 1b subgenomic replicon assay. AP89652 contains two chiral centers, and testing of two syn enantiomers revealed that ac... |
|
|
The role of calcium signalling in the chondrogenic response of mesenchymal stem cells to hydrostatic pressure.
Eur. Cell. Mater. 28 , 358-71, (2014) The object of this study was to elucidate the role of Ca++ signalling in the chondrogenic response of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to hydrostatic pressure (HP). MSCs were seeded into agarose hydrogels, subjected to HP or kept in free swelling conditions, and... |