奎宁; 无水奎宁; 金鸡纳碱; 金鸡纳霜
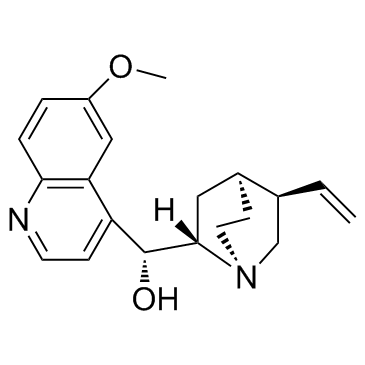
奎宁; 无水奎宁; 金鸡纳碱; 金鸡纳霜结构式

|
常用名 | 奎宁; 无水奎宁; 金鸡纳碱; 金鸡纳霜 | 英文名 | Quinine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 130-95-0 | 分子量 | 324.417 | |
| 密度 | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 495.9±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C20H24N2O2 | 熔点 | 176-177ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 253.7±27.3 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS08 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Enhancing perception of contaminated food through acid-mediated modulation of taste neuron responses.
Curr. Biol. 24(17) , 1969-77, (2014) Natural foods contain not only nutrients, but also nonnutritious and potentially harmful chemicals. Thus, animals need to evaluate food content in order to make adequate feeding decisions.Here, we investigate the effects of acids on the taste neuron responses... |
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of 8-O-Carboxymethylpyranine (CM-Pyranine) as a Bright, Violet-Emitting, Fluid-Phase Fluorescent Marker in Cell Biology.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0133518, (2015) To avoid spectral interference with common fluorophores in multicolor fluorescence microscopy, a fluid-phase tracer with excitation and emission in the violet end of the visible spectrum is desirable. CM-pyranine is easily synthesized and purified. Its excita... |
|
|
Glycation of human cortical and cancellous bone captures differences in the formation of Maillard reaction products between glucose and ribose.
PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0117240, (2015) To better understand some aspects of bone matrix glycation, we used an in vitro glycation approach. Within two weeks, our glycation procedures led to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) at the levels that corresponded to approx. 25-30 year... |
|
|
A direct role of collagen glycation in bone fracture.
J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 52 , 120-30, (2015) Non-enzymatic glycation (NEG) is an age-related process accelerated by diseases like diabetes, and causes the accumulation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs). NEG-mediated modification of bone's organic matrix, principally collagen type-I, has been imp... |
|
|
Association between non-enzymatic glycation, resorption, and microdamage in human tibial cortices.
Osteoporos. Int. 26(3) , 865-73, (2015) To better understand the association between different components of bone quality, we investigated the relationship among in vivo generated non-enzymatic glycation, resorption, and microdamage. The results showed negative correlation between advanced glycatio... |
|
|
Allosteric inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase thumb domain site II: structure-based design and synthesis of new templates.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18 , 2836-48, (2010) Chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections are a significant medical problem worldwide. The NS5B Polymerase of HCV plays a central role in virus replication and is a prime target for the discovery of new treatment options. We recently disclosed 1H-benzo[de]is... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Calculating virtual log P in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and its derived parameters deltalog P(N)(oct-alk) and log D(pH)(alk).
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 3269-79, (2005) Growing interest in the use of both the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and the difference between log P(N)(oct) (the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |