藜芦醛; 3,4-二甲氧基苯甲醛
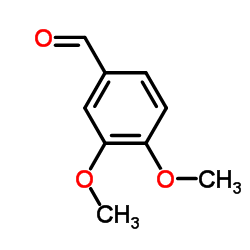
藜芦醛; 3,4-二甲氧基苯甲醛结构式

|
常用名 | 藜芦醛; 3,4-二甲氧基苯甲醛 | 英文名 | veratraldehyde |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 120-14-9 | 分子量 | 166.174 | |
| 密度 | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 281.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C9H10O3 | 熔点 | 40-43 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 110.4±8.2 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Sensitive naked eye detection of hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide by aza-BODIPY dyes in aqueous medium.
Anal. Chem. 86(18) , 9335-42, (2014) With an objective to develop optical probes for biologically important anions and neutral molecules, we synthesized three novel NIR absorbing aza-BODIPY derivatives, 3a-3c, and have systematically tuned their photophysical properties by changing the periphera... |
|
|
A chemical screening approach reveals that indole fluorescence is quenched by pre-fibrillar but not fibrillar amyloid-beta.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 4952-7, (2009) Aggregated amyloid-beta (Abeta) peptide is implicated in the pathology of Alzheimer's disease. In vitro and in vivo, these aggregates are found in a variety of morphologies, including globular oligomers and linear fibrils, which possess distinct biological ac... |
|
|
Stopped-Flow Enantioselective HPLC-CD Analysis and TD-DFT Stereochemical Characterization of Methyl Trans-3-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)Glycidate.
Chirality 27 , 914-8, (2015) Caffeic acid-derived polyethers are a class of natural products isolated from the root extracts of comfrey and bugloss, which are endowed with intriguing pharmacological properties as anticancer agents. The synthesis of new polyether derivatives is achieved t... |
|
|
Characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae YMR318C (ADH6) gene product as a broad specificity NADPH-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase: relevance in aldehyde reduction.
Biochem. J. 361(Pt 1) , 163-72, (2002) YMR318C represents an open reading frame from Saccharomyces cerevisiae with unknown function. It possesses a conserved sequence motif, the zinc-containing alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) signature, specific to the medium-chain zinc-containing ADHs. In the present... |
|
|
Antioxidant properties of 8.0.4'-neolignans.
Phytomedicine 8(6) , 454-9, (2001) A series of naturally occurring 8.0.4'-neolignans (1a-d, 1g, 2g, 2h) and their analogues (le-f, lh, 1i, 2a-f, 2i) have been synthesized in racemic form starting from commercially available phenols, such as eugenol, isoeugenol and 4-allyl-2,6-dimethoxyphenol a... |
|
|
[Dependence of activities of polysaccharide hydrolases and oxidases from Cerrena unicolor on the source of carbon and aromatic acids in culture media].
Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 38(3) , 243-7, (2002) The activities of carboxymethylcellulase and xylanase in the higher basidial fungus Cerrena unicolor grown in avicel-containing medium reached 1.95 and 1.50 units per mg protein, respectively, whereas in mannitol-containing medium they ranged from 0.02 to 0.0... |
|
|
Identification of phenolics for control of Aspergillus flavus using Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a model target-gene bioassay.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 52(26) , 7814-21, (2004) The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae was used in a high-throughput bioassay to identify phenolic agents for control of the aflatoxigenic fungus Aspergillus flavus. Veratraldehyde, 1, cinnamic acid, 5, and the respective benzoic acid derivatives vanillin, 2, van... |
|
|
Electroenzymatic oxidation of veratryl alcohol by lignin peroxidase.
J. Biotechnol. 102(3) , 261-8, (2003) This paper reports the formation of veratraldehyde by electroenzymatic oxidation of veratryl alcohol (3,4-dimethoxybenzyl alcohol) hybridizing both electrochemical and enzymatic reactions and using lignin peroxidase. The novel electroenzymatic method was foun... |
|
|
Combinatorial evaluation of laccase-mediator system in the oxidation of veratryl alcohol.
Biotechnol. Lett. 35(2) , 225-31, (2013) Laccases play an important role in the biological break down of lignin and have great potential in the deconstruction of lignocellulosic feedstocks. We examined 16 laccases, both commercially prepared and crude extracts, for their ability to oxidize veratryl ... |
|
|
Methyl jasmonate modulated biotransformation of phenylpropanoids to vanillin related metabolites using Capsicum frutescens root cultures.
Plant Physiol. Biochem. 43(2) , 125-31, (2005) Normal root cultures of Capsicum frutescens biotransform externally fed precursors, like caffeic acid and veratraldehyde, to vanillin and other related metabolites. The bioconversion of caffeic acid to further metabolites--viz. vanillin, vanillylamine, vanill... |