甲苯氟磺胺
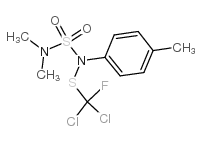
甲苯氟磺胺结构式

|
常用名 | 甲苯氟磺胺 | 英文名 | dichloro-N-[(dimethylamino)sulphonyl]fluoro-N-(p-tolyl)methanesulphenamide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 731-27-1 | 分子量 | 347.25700 | |
| 密度 | 1.505g/cm3 | 沸点 | 366ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C10H13Cl2FN2O2S2 | 熔点 | 96°C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 175.1ºC | |
| 符号 |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Baby food production chain: pesticide residues in fresh apples and products.
Food Addit. Contam. 22(12) , 1231-42, (2005) During 3 years of a monitoring programme, 522 samples of fresh apples, six brands of fruit purées and various types of fruit baby food prepared from these materials were analysed. Each sample was examined for the presence of 86 GC amenable pesticide residues.... |
|
|
[Occurrence of pesticide residues in raspberries in 2000-2005].
Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 58(3) , 509-13, (2007) The aim of this paper was to present occurrence of pesticide residues in raspberries in 2000-2005. Gas chromatographic and spectroscopy methods were used. The most frequently found were tolylfluanid residues (43% of the analysed samples), procymidone residues... |
|
|
Exposure to fungicides in fruit growing: re-entry time as a predictor for dermal exposure.
Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 60(6) , 789-93, (1999) As part of a European Concerted Action on Male Reproduction Capability an exposure assessment survey was conducted among seasonal workers in the fruit growing sector in the Netherlands. Dermal exposure to the fungicides captan and tolylfluanid was measured us... |
|
|
Processing factors and variability of pyrimethanil, fenhexamid and tolylfluanid in strawberries.
Food Addit. Contam. 20(8) , 728-41, (2003) An HPLC-MS/MS method for the analysis of three pesticides in strawberries was developed and validated. Recoveries were measured at three spiking levels and ranged from 85 to 99% (mean recoveries). The effects of processing of strawberries ranging from rinsing... |
|
|
Xenobiotics and the glucocorticoid receptor: additive antagonistic effects on tyrosine aminotransferase activity in rat hepatoma cells.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 96(4) , 309-15, (2005) Methylsulfonyl-PCBs (MeSO2-PCBs) and some fungicides were studied for their functional effects on the glucocorticoid signal transduction in the Reuber rat hepatoma H-II-E-C3 cell line. 4-Substituted MeSO2-PCBs, tolylfluanid and ketoconazole displayed antagoni... |
|
|
Phytotoxicity of tolylfluanid in tomatoes.
Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 71(2 Pt A) , 79-82, (2006) The use of Euparen Multi (tolylfluanid) for controlling Botrytis cinerea in tomatoes has been decreased the last decade for several reasons. Because of the lack of different fungicides with a good efficacy it is important that growers can use different fungic... |
|
|
Comparative toxicity of alternative antifouling biocides on embryos and larvae of marine invertebrates.
Sci. Total Environ. 367(2-3) , 573-85, (2006) This study evaluates the impact of commonly used "booster" biocides (chlorothalonil, Sea-Nine 211, dichlofluanid, tolylfluanid and Irgarol 1051) on early developmental stages of marine invertebrates of commercial and ecological relevance. Toxicity tests were ... |
|
|
Booster biocides and microfouling.
Biofouling 26(7) , 787-98, (2010) Antifouling (AF) paints are used to prevent the attachment of living organisms to the submerged surfaces of ships, boats and aquatic structures, usually by the release of biocides. Apart from copper, organic booster biocides are the main active components in ... |
|
|
The novel endocrine disruptor tolylfluanid impairs insulin signaling in primary rodent and human adipocytes through a reduction in insulin receptor substrate-1 levels.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1822(6) , 952-60, (2012) Emerging data suggest that environmental endocrine disrupting chemicals may contribute to the pathophysiology of obesity and diabetes. In a prior work, the phenylsulfamide fungicide tolylfluanid (TF) was shown to augment adipocyte differentiation, yet its eff... |
|
|
Fate of the fungicide tolylfluanid in the pear cold stored in controlled or non controlled atmosphere.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 46(4) , 499-506, (1991)
|