6-姜烯酚
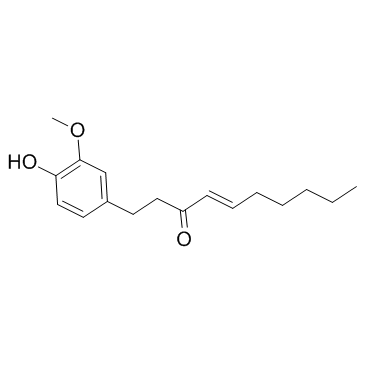
6-姜烯酚结构式

|
常用名 | 6-姜烯酚 | 英文名 | 6-Shogaol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 555-66-8 | 分子量 | 276.371 | |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 427.5±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C17H24O3 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 150.3±19.4 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Update on the chemopreventive effects of ginger and its phytochemicals.
Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr 51(6) , 499-523, (2011) The rhizomes of Zingiber officinale Roscoe (Zingiberaceae), commonly known as ginger, is one of the most widely used spice and condiment. It is also an integral part of many traditional medicines and has been extensively used in Chinese, Ayurvedic, Tibb-Unani... |
|
|
In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of 1-dehydro-[6]-gingerdione, 6-shogaol, 6-dehydroshogaol and hexahydrocurcumin.
Food Chem. 135(2) , 332-7, (2012) Hexahydrocurcumin, 1-dehydro-[6]-gingerdione, 6-dehydroshogaol and 6-shogaol were evaluated for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities in the present study. The relative antioxidant potencies of ginger compounds decreased in similar order of 1-deh... |
|
|
6-Shogaol inhibits breast and colon cancer cell proliferation through activation of peroxisomal proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ).
Cancer Lett. 336(1) , 127-39, (2013) 6-Shogaol has been shown to possess many antitumor properties including inhibition of cancer cell growth, inhibition of cancer metastasis, induction of apoptosis in cancer cells and induction of cancer cell differentiation. Despite its prominent antitumor eff... |
|
|
Effects of [6]-shogaol on cholinergic signaling in HT22 cells following neuronal damage induced by hydrogen peroxide.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 50(5) , 1454-9, (2012) Cholinergic neurons play a major role in memory and attention. The dysfunction and death of these neurons, especially in the hippocampus, are thought to contribute to the pathophysiology of memory deficits associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Therefore, ... |
|
|
Effects of ginger constituents on the gastrointestinal tract: role of cholinergic M3 and serotonergic 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptors.
Planta Med. 77(10) , 973-8, (2011) The herbal drug ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) may be effective for treating nausea, vomiting, and gastric hypomotility. In these conditions, cholinergic M (3) receptors and serotonergic 5-HT (3) and 5-HT (4) receptors are involved. The major chemical co... |
|
|
Preparation of the monomers of gingerols and 6-shogaol by flash high speed counter-current chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1218(36) , 6187-90, (2011) The flash high speed counter-current chromatographic (FHSCCC) separation of gingerols and 6-shogaol was performed on a HSCCC instrument equipped with a 1200-ml column (5 mm tubing i.d.) at a flow rate of 25 ml/min. The performance met the FHSCCC feature that ... |
|
|
6-shogaol-rich extract from ginger up-regulates the antioxidant defense systems in cells and mice.
Molecules 17(7) , 8037-55, (2012) The rhizome of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) is known to have several bioactive compounds including gingerols and shogaols which possess beneficial health properties such as anti-inflammatory and chemopreventive effects. Based on recent observations tha... |
|
|
Protection by [6]-shogaol against lipopolysaccharide-induced toxicity in murine astrocytes is related to production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 50(3-4) , 597-602, (2012) [6]-Shogaol has beneficial effects in spinal neuronal regeneration, but associated molecules and mechanisms are not identified. Neurotrophic factors, including brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), are associated with proliferation and differentiation of ... |
|
|
Metabolites of ginger component [6]-shogaol remain bioactive in cancer cells and have low toxicity in normal cells: chemical synthesis and biological evaluation.
PLoS ONE 8(1) , e54677, (2013) Our previous study found that [6]-shogaol, a major bioactive component in ginger, is extensively metabolized in cancer cells and in mice. It is unclear whether these metabolites retain bioactivity. The aim of the current study is to synthesize the major metab... |
|
|
Enhanced CD36 expression changes the role of Nrf2 activation from anti-atherogenic to pro-atherogenic in apoE-deficient mice.
Atherosclerosis 225(1) , 83-90, (2012) Oxidative stress has been implicated as a causative factor of atherosclerosis. Defense systems against oxidative stress are maintained by radical scavenging antioxidants and/or by regulating the expression of antioxidant genes by activating oxidative stress-s... |