腺苷酸基琥珀酸
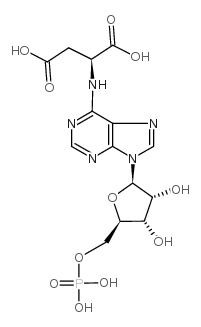
腺苷酸基琥珀酸结构式

|
常用名 | 腺苷酸基琥珀酸 | 英文名 | Adenylosuccinic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 19046-78-7 | 分子量 | 463.29300 | |
| 密度 | 2.19g/cm3 | 沸点 | 921.9ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C14H18N5O11P | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 511.3ºC |
|
The RimL transacetylase provides resistance to translation inhibitor microcin C.
J. Bacteriol. 196(19) , 3377-85, (2014) Peptide-nucleotide antibiotic microcin C (McC) is produced by some Escherichia coli strains. Inside a sensitive cell, McC is processed, releasing a nonhydrolyzable analog of aspartyl-adenylate, which inhibits aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. The product of mccE, a g... |
|
|
Synthesis and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitory activity of aspartyl adenylate analogs.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13(1) , 69-75, (2005) Three nonhydrolyzable aspartyl adenylate analogs have been prepared and tested as inhibitors of E. coli aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. 5'-O-[N-(L-Aspartyl)sulfamoyl]adenosine is a potent competitive inhibitor (K(i) = 15 nM) whereas L-aspartol adenylate is a weaker... |
|
|
MccE provides resistance to protein synthesis inhibitor microcin C by acetylating the processed form of the antibiotic.
J. Biol. Chem. 285(17) , 12662-9, (2010) The heptapeptide-nucleotide microcin C (McC) is a potent inhibitor of enteric bacteria growth. McC is excreted from producing cells by the MccC transporter. The residual McC that remains in the producing cell can be processed by cellular aminopeptidases with ... |
|
|
[Aspartyladenylate analog--effective inhibitor of asparagine synthetase].
Bioorg. Khim. 14(7) , 969-72, (1988) A number of earlier unknown phosphonate analogues of aspartyl adenylate with anhydride oxygen substituted by --CH2--, and the carbonyl group substituted by --CH(OH)- or --CH(NH2)-groups were synthesized. These compounds were used to study the reaction mechani... |
|
|
Escherichia coli peptidase A, B, or N can process translation inhibitor microcin C.
J. Bacteriol. 190(7) , 2607-10, (2008) The heptapeptide-nucleotide microcin C (McC) targets aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. Upon its entry into a susceptible cell, McC is processed to release a nonhydrolyzable aspartyl-adenylate that inhibits aspartyl-tRNA synthetase, leading to the cessation of transla... |
|
|
Aspartyl tRNA-synthetase from Escherichia coli: flexibility and adaptability to the substrates.
J. Mol. Biol. 299(5) , 1157-64, (2000) The crystal structure of aspartyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli has been determined to a resolution of 2.7 A. The structure is compared to the same enzyme co-crystallized with tRNA(Asp) and containing aspartyl adenylate or ATP. The asymmetric unit con... |
|
|
Inhibition by L-aspartol adenylate of a nondiscriminating aspartyl-tRNA synthetase reveals differences between the interactions of its active site with tRNA(Asp) and tRNA(Asn).
J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 22(1) , 77-82, (2007) Asparaginyl-tRNA formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 involves a nondiscriminating aspartyl-tRNA synthetase (ND-AspRS) which forms Asp-tRNA(Asp) and Asp-tRNA(Asn), and a tRNA-dependent amidotransferase which transamidates the latter into Asn-tRNA(Asn). We... |
|
|
Covalent aspartylation of aspartyl-tRNA synthetase from bakers' yeast by its cognate aspartyl adenylate: identification of the labeled residues.
Biochemistry 26(7) , 2054-9, (1987) Aspartyl-tRNA synthetase from bakers' yeast gives an unstable complex with the cognate adenylate, which reacts after dissociation with amino acid side chains of the protein. This leads to a covalent incorporation of aspartic acid into aspartyl-tRNA synthetase... |