顺-1,2-二氯乙烯标准溶液
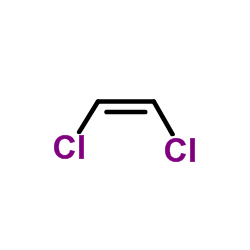
顺-1,2-二氯乙烯标准溶液结构式

|
常用名 | 顺-1,2-二氯乙烯标准溶液 | 英文名 | (Z)-1,2-Dichloroethene |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 156-59-2 | 分子量 | 96.943 | |
| 密度 | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 47.7±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C2H2Cl2 | 熔点 | -80ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 6.1±0.0 °C | |
| 符号 |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Implications of soil mixing for NAPL source zone remediation: Column studies and modeling of field-scale systems.
J. Contam. Hydrol. 177-178 , 206-19, (2015) Soil remediation is often inhibited by subsurface heterogeneity, which constrains contaminant/reagent contact. Use of soil mixing techniques for reagent delivery provides a means to overcome contaminant/reagent contact limitations. Furthermore, soil mixing re... |
|
|
Demonstration of compound-specific isotope analysis of hydrogen isotope ratios in chlorinated ethenes.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(3) , 1461-7, (2013) High-temperature pyrolysis conversion of organic analytes to H(2) in hydrogen isotope ratio compound-specific isotope analysis (CSIA) is unsuitable for chlorinated compounds such as trichloroethene (TCE) and cis-1,2-dichloroethene (DCE), due to competition fr... |
|
|
Degradation product partitioning in source zones containing chlorinated ethene dense non-aqueous-phase liquid.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 44(23) , 9105-11, (2010) Abiotic and biotic reductive dechlorination with chlorinated ethene dense non-aqueous-phase liquid (DNAPL) source zones can lead to significant fluxes of complete and incomplete transformation products. Accurate assessment of in situ rates of transformation a... |
|
|
Trichloroethene and cis-1,2-dichloroethene concentration-dependent toxicity model simulates anaerobic dechlorination at high concentrations. II: continuous flow and attached growth reactors.
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 107(3) , 540-9, (2010) A model that was used to describe toxicity from high concentrations of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons (CAHs) on reductively dechlorinating cultures in batch reactors (Sabalowsky and Semprini (in press)) was extended here to simulate observations in contin... |
|
|
Simultaneous counter-flow of chlorinated volatile organic compounds across the saturated-unsaturated interface region of an aquifer.
Water Res. 44(7) , 2107-12, (2010) Concentrations of chlorinated volatile organic compounds (Cl-VOCs) at the saturated-unsaturated interface region (SUIR; depth of approximately 18m) of a sandy phreatic aquifer were measured in two monitoring wells located 25m apart. The concentrations of the ... |
|
|
Characterization of microbial community structure and population dynamics of tetrachloroethene-dechlorinating tidal mudflat communities.
Biodegradation 22(4) , 687-98, (2011) Tetrachloroethene (PCE) and trichloroethene (TCE) are common groundwater contaminants that also impact tidal flats, especially near urban and industrial areas. However, very little is known about dechlorinating microbial communities in tidal flats. Titanium p... |
|
|
Isolation and characterization of tetrachloroethylene- and cis-1,2-dichloroethylene-dechlorinating propionibacteria.
J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38(10) , 1667-77, (2011) Two rapidly growing propionibacteria that could reductively dechlorinate tetrachloroethylene (PCE) and cis-1,2-dichloroethylene (cis-DCE) to ethylene were isolated from environmental sediments. Metabolic characterization and partial sequence analysis of their... |
|
|
Cytochrome P450 initiates degradation of cis-dichloroethene by Polaromonas sp. strain JS666.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 79(7) , 2263-72, (2013) Polaromonas sp. strain JS666 grows on cis-1,2-dichoroethene (cDCE) as the sole carbon and energy source under aerobic conditions, but the degradation mechanism and the enzymes involved are unknown. In this study, we established the complete pathway for cDCE d... |
|
|
Anaerobic abiotic transformations of cis-1,2-dichloroethene in fractured sandstone.
Chemosphere 90(8) , 2226-32, (2013) A fractured sandstone aquifer at an industrial site is contaminated with trichloroethene to depths greater than 244 m. Field data indicate that trichloroethene is undergoing reduction to cis-1,2-dichloroethene (cDCE); vinyl chloride and ethene are present at ... |
|
|
Robustness of an aerobic metabolically vinyl chloride degrading bacterial enrichment culture.
Water Sci. Technol. 64(9) , 1796-803, (2011) Degradation of the lower chlorinated ethenes is crucial to the application of natural attenuation or in situ bioremediation on chlorinated ethene contaminated sites. Recently, within mixtures of several chloroethenes as they can occur in contaminated groundwa... |