2-溴乙胺氢溴酸盐
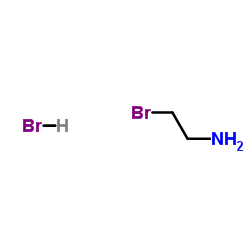
2-溴乙胺氢溴酸盐结构式

|
常用名 | 2-溴乙胺氢溴酸盐 | 英文名 | 2-Bromoethylamine hydrobromide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 2576-47-8 | 分子量 | 204.892 | |
| 密度 | 1.581g/cm3 | 沸点 | 131.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C2H7Br2N | 熔点 | 172 °C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 33.5ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Synthesis of 4-thia-[6-(13)C]lysine from [2- (13)C]glycine: access to site-directed isotopomers of 2-aminoethanol, 2-bromoethylamine and 4-thialysine.
Amino Acids 42(1) , 309-15, (2012) 4-Thialysine (S-(2-aminoethyl)-L: -cysteine) is an analog of lysine. It has been used as an alternative substrate for lysine in enzymatic reactions. Site-directed isotopomers are often needed for elucidation of mechanism of reactions. 4-Thialysine can be synt... |
|
|
Selectivity of labeled bromoethylamine for protein alkylation.
J. Mol. Model. 18(9) , 4547-56, (2012) Alkylation of cysteine residues has been used extensively for characterization of proteins and their mode of action in biological systems, research endeavors that are at the core of proteomics. Treatment with a simple alkylating agent such as [2-(13)C] bromoe... |
|
|
Protective humoral immune response induced by an inactivated porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus expressing the hypo-glycosylated glycoprotein 5.
Vaccine 32(29) , 3617-22, (2014) Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) causes significant economic losses to the swine industry worldwide. Although inactivated and live vaccines are commercially available for the control of PRRS, both types of vaccine have not always proven su... |
|
|
Prediction of nephrotoxicant action and identification of candidate toxicity-related biomarkers.
Toxicol. Pathol. 33(3) , 343-55, (2005) A vast majority of pharmacological compounds and their metabolites are excreted via the urine, and within the complex structure of the kidney,the proximal tubules are a main target site of nephrotoxic compounds. We used the model nephrotoxicants mercuric chlo... |
|
|
Studies on the acute biochemical effects of La(NO3)3 using 1H NMR spectroscopy of urine combined with pattern recognition.
J. Inorg. Biochem. 99(2) , 644-50, (2005) (1)H NMR spectroscopic and pattern recognition-based methods were applied to the studies on the acute biochemical effects of La(NO(3))(3). Male Wistar rats were separated into groups (n=10) and each was treated with one of following compounds, sodium chromate... |
|
|
Toxicogenomic biomarkers for renal papillary injury in rats.
Toxicology 303 , 1-8, (2013) Renal papillary injury is a common side effect observed during nonclinical and clinical investigations in drug development. The present study aimed to identify genomic biomarkers for early and sensitive detection of renal papillary injury in rats. We hypothes... |
|
|
Characterization of renal papillary antigen 1 (RPA-1), a biomarker of renal papillary necrosis.
Toxicol. Pathol. 38(3) , 346-58, (2010) Renal papillary necrosis (RPN) is a relatively common toxicity observed in preclinical drug safety testing. It is also observed in a variety of human diseases. RPN is difficult to diagnose without expensive scanning methods or histopathology. A noninvasive bi... |
|
|
Application of Dolichos biflorus in immunoassay detection of kidney collecting duct biomarkers.
Biomarkers 15 , 424-35, (2010) Currently there are no biomarkers for detecting collecting duct damage in man. Antibodies to several collecting duct-specific antigens exist but sandwich assays have been difficult to establish due to the need for two different antibodies to the same protein.... |
|
|
Allopurinol suppresses 2-bromoethylamine and 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP(+))-induced hydroxyl radical generation in rat striatum.
Toxicology 218(1) , 75-9, (2006) The present study was examined whether or not 2-bromoethyamine, a semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO, EC; 1.4.3.6) inhibitor, would increase an active dopaminergic neurotoxin, 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP(+))-induced hydroxyl radical ((*)OH) ... |
|
|
Effects of 2-bromoethanamine on TonEBP expression and its possible role in induction of renal papillary necrosis in mice.
Toxicol. Sci. 118(2) , 510-20, (2010) Chronic analgesic abuse has been shown to induce severe renal injury characterized by renal papillary necrosis (RPN), an injury detectable at late stage. While direct toxicity of the drug may exist, the molecular mechanisms underlying analgesics induction of ... |