色甘酸钠
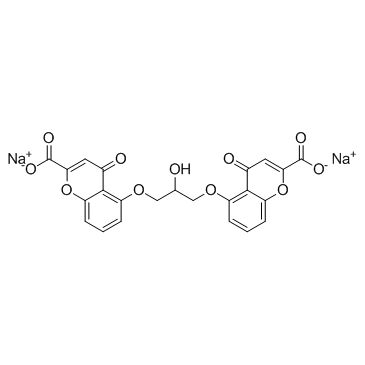
色甘酸钠结构式

|
常用名 | 色甘酸钠 | 英文名 | Cromolyn (sodium) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 15826-37-6 | 分子量 | 512.330 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | 752.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C23H14Na2O11 | 熔点 | 241-2420C (dec) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 263.9ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Chronic pelvic allodynia is mediated by CCL2 through mast cells in an experimental autoimmune cystitis model.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 308(2) , F103-13, (2015) The cause of chronic pelvic pain in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome (IC/PBS) remains unclear; autoimmunity is a possible etiology. We have recently shown that injection of a single immunogenic peptide of uroplakin 3A (UPK3A 65-84) induces exper... |
|
|
Psychological stress and corticotropin-releasing hormone increase intestinal permeability in humans by a mast cell-dependent mechanism.
Gut 63(8) , 1293-9, (2014) Intestinal permeability and psychological stress have been implicated in the pathophysiology of IBD and IBS. Studies in animals suggest that stress increases permeability via corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)-mediated mast cell activation. Our aim was to ... |
|
|
Inhibition of mast cell-derived histamine secretion by cromolyn sodium treatment decreases biliary hyperplasia in cholestatic rodents.
Lab. Invest. 94(12) , 1406-18, (2014) Cholangiopathies are characterized by dysregulation of the balance between biliary growth and loss. We have shown that histamine (HA) stimulates biliary growth via autocrine mechanisms. To evaluate the paracrine effects of mast cell (MC) stabilization on bili... |
|
|
Evidence questioning cromolyn's effectiveness and selectivity as a 'mast cell stabilizer' in mice.
Lab. Invest. 92(10) , 1472-82, (2012) Cromolyn, widely characterized as a 'mast cell stabilizer', has been used in mice to investigate the biological roles of mast cells in vivo. However, it is not clear to what extent cromolyn can either limit the function of mouse mast cells or influence biolog... |
|
|
Inhibiting mast cell degranulation by HO-1 affects dendritic cell maturation in vitro.
Inflamm. Res. 63(7) , 527-37, (2014) Mast cell (MC) degranulation can break peripheral immune tolerance. However, its mechanism remains unclear. Our goal was to study the stabilization of MC membranes by heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in order to influence dendritic cell (DC) function.Mast cells and de... |
|
|
Anti-inflammatory gallic Acid and wedelolactone are G protein-coupled receptor-35 agonists.
Pharmacology 89(3-4) , 211-9, (2012) G protein-coupled receptor-35 (GPR35) has been shown to be a target of the asthma drugs cromolyn disodium and nedocromil sodium. Gallic acid and caffeic acids are reported to modulate allergic reactions via unknown mode(s) of action. Here we attempt to elucid... |
|
|
Mast cells promote blood brain barrier breakdown and neutrophil infiltration in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia.
J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 35(4) , 638-47, (2015) Blood brain barrier (BBB) breakdown and neuroinflammation are key events in ischemic stroke morbidity and mortality. The present study investigated the effects of mast cell deficiency and stabilization on BBB breakdown and neutrophil infiltration in mice afte... |
|
|
Choroidal mast cells in retinal pathology: a potential target for intervention.
Am. J. Pathol. 185 , 2083-95, (2015) Mast cells are important in the initiation of ocular inflammation, but the consequences of mast cell degranulation on ocular pathology remain uncharacterized. We induced mast cell degranulation by local subconjunctival injection of compound 48/80. Initial deg... |
|
|
Pharmaco-modulations of induced edema and vascular permeability changes by Vipera lebetina venom: inflammatory mechanisms.
Inflammation 36(2) , 434-43, (2013) The inflammatory response induced by Vipera lebetina venom (VLV) in the mice hind paw was evaluated by paw edema value and vascular permeability changes. The edema was produced in a dose- and time-dependent manner. This response was maximal within 2 h and dis... |
|
|
Mast cells activation contribute to small intestinal ischemia reperfusion induced acute lung injury in rats
Injury 43(8) , 1250-6, (2012) Background Small intestinal ischemia-reperfusion (IIR) injury may lead to severe local and remote tissue injury, especially acute lung injury (ALI). Mast cell activation plays an important role in IIR injury. It is unknown whether IIR mediates lung injury via... |