Ro 41-5253
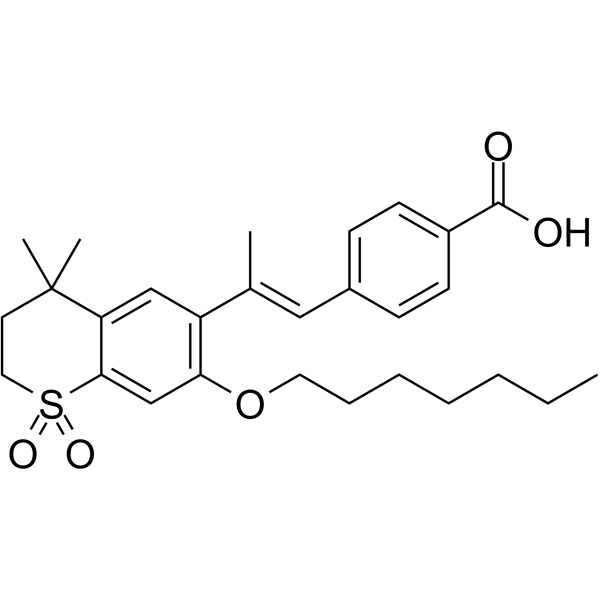
Ro 41-5253结构式

|
常用名 | Ro 41-5253 | 英文名 | Ro 41-5253 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 144092-31-9 | 分子量 | 484.64700 | |
| 密度 | 1.154g/cm3 | 沸点 | 661.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C28H36O5S | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 353.8ºC |
|
Effect of all-trans-retinoic acid on enterovirus 71 infection in vitro.
Br. J. Nutr. 111(9) , 1586-93, (2014) Our previous studies have shown that vitamin A (VA) status is associated with antiviral immunity and pathogenic conditions in enterovirus 71 (EV71)-infected children. In the present study, we established an in vitro model to investigate the effects and potent... |
|
|
Retinoic acid inhibits in vivo interleukin-2 gene expression and T-cell activation in mice.
Immunology 126(4) , 514-22, (2009) Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is an essential cytokine for T-lymphocyte homeostasis. We have previously reported that all-trans retinoic acid (atRA) enhances the secretion of IL-2 from human peripheral blood T cells in vitro, followed by increased proliferation and in... |
|
|
Overexpression of mucin genes induced by interleukin-1 beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, lipopolysaccharide, and neutrophil elastase is inhibited by a retinoic acid receptor alpha antagonist.
Exp. Lung Res. 28(4) , 315-32, (2002) Proinflammatory cytokines, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and neutrophil elastase (NE) have been implicated in the induction of hypersecretion of respiratory mucus. In this study, we demonstrated that interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) increased MUC2 and MUC5AC mRNA lev... |
|
|
Retinoic acid signaling is necessary for the development of the organ of Corti.
Dev. Biol. 213(1) , 180-93, (1999) The cellular mosaic of the mammalian organ of Corti represents one of the most highly ordered structures in any vertebrate system. A single row of inner hair cells and three or four rows of outer hair cells extend along the basal-to-apical axis of the cochlea... |
|
|
Retinoids and human breast cancer: in vivo effects of an antagonist for RAR-alpha.
Cancer Lett. 219(1) , 27-31, (2005) The aim of the present study was to evaluate the in vivo effects of the RAR-alpha selective antagonist Ro 41-5253 on a xenograft animal model for breast cancer. Our observations indicate a lack of toxic side effects of the drug, even when used at high dosages... |
|
|
A putative G-protein-coupled receptor, H218, is down-regulated during the retinoic acid-induced differentiation of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells.
Exp. Cell Res. 239(2) , 320-5, (1998) We have previously cloned a novel guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G-protein)-coupled receptor, H218, that has sequence similarity to a lysophosphatidic acid receptor, edg2. We present here Northern analysis indicating that the H218 mRNA is expressed in un... |
|
|
The Retinoic Acid Receptor-alpha mediates human T-cell activation and Th2 cytokine and chemokine production.
BMC Immunol. 9 , 16, (2008) We have recently demonstrated that all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) and 9-cis-retinoic acid (9-cis RA) promote IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 synthesis, while decreasing IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha expression by activated human T cells and reduces the synthesis of IL-12p70 f... |
|
|
Critical role of the H6-H7 loop in the conformational adaptation of all-trans retinoic acid and synthetic retinoids within the ligand-binding site of RARalpha.
J. Mol. Endocrinol. 24(3) , 353-64, (2000) The pleiotropic effects of the natural and synthetic retinoids are mediated by the activation of the two subfamilies of nuclear receptors, the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and the retinoic X receptors (RXRs). At the molecular level, these events begin with ... |
|
|
Anticoagulant effects of synthetic retinoids.
Leuk. Lymphoma 31(1-2) , 71-80, (1998) We have recently found that retinoic acids (RAs) evoke anticoagulant effect by upregulating thrombomodulin (TM) and downregulating tissue factor (TF) expression in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) and monoblastic leukemia cells. Two classes of nuclear RA re... |
|
|
Histone deacetylase inhibitors enhance retinoid response in human breast cancer cell lines.
Anticancer Res. 24(6) , 4019-24, (2004) Solid tumors develop resistance to retinoids during carcinogenesis. One of the strategies to overcome this resistance may include the combination of these molecules with other differentiating, cytotoxic or chromatin-remodelling agents. We analysed the anti-pr... |