Histone deacetylase inhibitors enhance retinoid response in human breast cancer cell lines.
Laura Emionite, Fabia Galmozzi, Myriam Grattarola, Francesco Boccardo, Laura Vergani, Salvatore Toma
文献索引:Anticancer Res. 24(6) , 4019-24, (2004)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Solid tumors develop resistance to retinoids during carcinogenesis. One of the strategies to overcome this resistance may include the combination of these molecules with other differentiating, cytotoxic or chromatin-remodelling agents. We analysed the anti-proliferative activity of two histone-deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs), Trichostatin A (TSA) and sodium phenylbutyrate (PB), alone or combined with retinoids, all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and Ro 41-5253, on two human breast cancer cell lines: the hormone-dependent MCF-7 and the hormone-independent MDA-MB-231. These lines responded differently to retinoids: MCF-7 were sensitive, whilst MDA-MB-231 were rather resistant. When the retinoids were combined with HDACIs, these molecules potentiated the retinoid activity on growth inhibition, especially for the association Ro 41-5253 and TSA. By FACS analysis, we observed that the anti-proliferative effects were only partially due to pro-apopotic mechanisms, suggesting a cell-cycle block. The efficacy of the retinoids/HDACIs combinations could represent a new strategy in breast cancer chemotherapy, allowing inhibition of both ER + and ER- cell populations.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
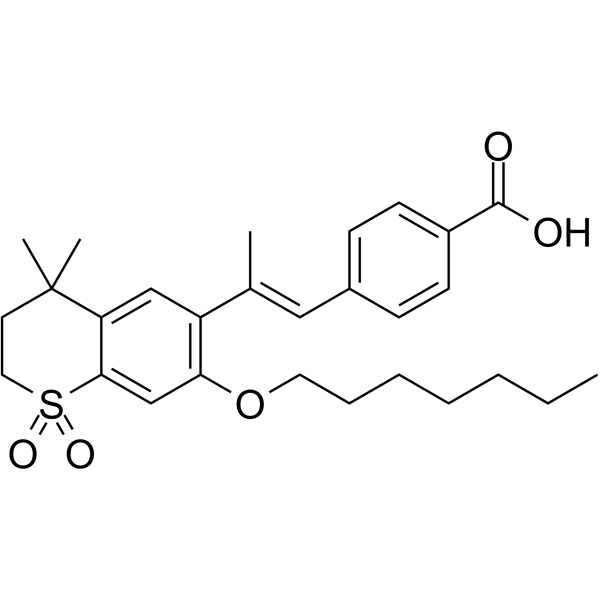 |
Ro 41-5253
CAS:144092-31-9 |
C28H36O5S |
|
Effect of all-trans-retinoic acid on enterovirus 71 infectio...
2014-05-01 [Br. J. Nutr. 111(9) , 1586-93, (2014)] |
|
Retinoic acid inhibits in vivo interleukin-2 gene expression...
2009-04-01 [Immunology 126(4) , 514-22, (2009)] |
|
Overexpression of mucin genes induced by interleukin-1 beta,...
2002-06-01 [Exp. Lung Res. 28(4) , 315-32, (2002)] |
|
Retinoic acid signaling is necessary for the development of ...
1999-09-01 [Dev. Biol. 213(1) , 180-93, (1999)] |
|
Retinoids and human breast cancer: in vivo effects of an ant...
2005-02-28 [Cancer Lett. 219(1) , 27-31, (2005)] |