Z-L-Lys-SBzl盐酸盐
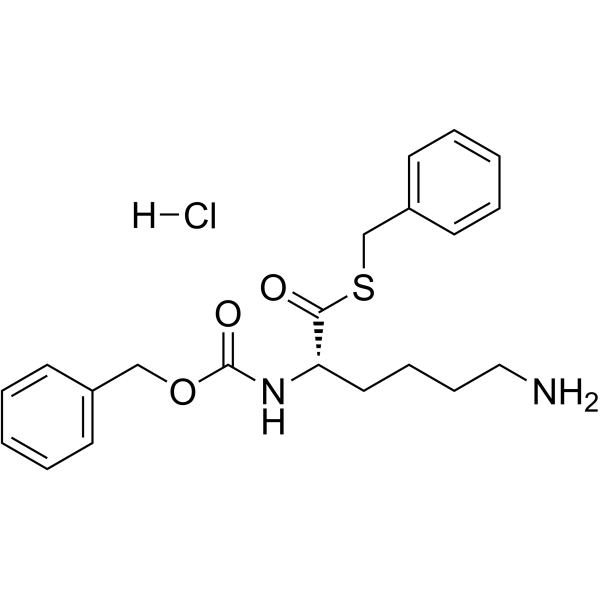
Z-L-Lys-SBzl盐酸盐结构式

|
常用名 | Z-L-Lys-SBzl盐酸盐 | 英文名 | Z-LYS-SBZL HCL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 69861-89-8 | 分子量 | 422.96900 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | 566.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C21H27ClN2O3S | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 296.3ºC |
|
Granzymes (lymphocyte serine proteases): characterization with natural and synthetic substrates and inhibitors.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1477 , 307-323, (2000) Natural killer (NK) and cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs) kill cells within an organism to defend it against viral infections and the growth of tumors. One mechanism of killing involves exocytosis of lymphocyte granules which causes pores to form in the membrane... |
|
|
2-chloroadenosine stimulates granule exocytosis from mouse natural killer cells: evidence for signal transduction through a novel extracellular receptor.
Exp. Cell Res. 233 , 187-197, (1997) The effect of 2-chloroadenosine (2CA), an adenosine receptor agonist, on the activation status of mouse natural killer (NK) cells was determined. Splenic lymphocytes incubated with 2CA exocytosed an NK cell-associated granzyme with N alpha-CBZ-L-lysine thiobe... |
|
|
Natural killer cell lytic granule secretion occurs through a pervasive actin network at the immune synapse.
PLoS Biol. 9 , e1001151, (2011) Accumulation of filamentous actin (F-actin) at the immunological synapse (IS) is a prerequisite for the cytotoxic function of natural killer (NK) cells. Subsequent to reorganization of the actin network, lytic granules polarize to the IS where their contents ... |
|
|
Antioxidants, Enzyme Inhibitors, and Biogenic Compounds in Grain Extracts of Barleys.
Chem. Biodivers. 12 , 1678-95, (2015) The content of biogenic compounds and the biological activities of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.)-grain extracts was evaluated. The sufficiently large and heterogeneous set of barley genotypes (100 accessions) enabled the selection of special genotypes interesti... |
|
|
The major component of Na-CBZ-L-lysine thiobenzyl ester (BLT)-specific proteases in cytoplasmic granules of murine intraepithelial lymphocytes is granzyme A. Kato Y, Yokochi T, Sasaki K, et al.
Immunobiol. 196 , 465-474, (1997)
|