N-芴甲氧羰基-D-1,2,3,4-四氢异喹啉-3-羧酸
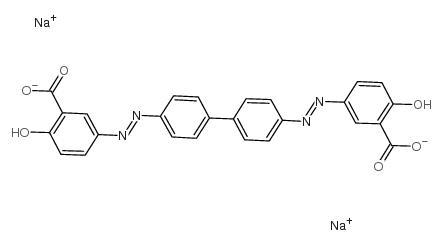
N-芴甲氧羰基-D-1,2,3,4-四氢异喹啉-3-羧酸结构式

|
常用名 | N-芴甲氧羰基-D-1,2,3,4-四氢异喹啉-3-羧酸 | 英文名 | CHRYSAMINE G |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 6472-91-9 | 分子量 | 526.40800 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | 711.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C26H16N4Na2O6 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 384ºC |
|
Imaging Abeta plaques in living transgenic mice with multiphoton microscopy and methoxy-X04, a systemically administered Congo red derivative.
J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 61 , 797-805, (2002) The identification of amyloid deposits in living Alzheimer disease (AD) patients is important for both early diagnosis and for monitoring the efficacy of newly developed anti-amyloid therapies. Methoxy-X04 is a derivative of Congo red and Chrysamine-G that co... |
|
|
Amyloid binding ligands as Alzheimer's disease therapies.
Neurobiol. Aging 23 , 1039-1042, (2002) Extracellular senile plaques (SPs) are hallmark brain lesions of sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD) and the likely consequence of genetic mutations that cause familial AD by increasing production of amyloidogenic amyloid-beta (Abeta). Although Abeta vaccines a... |
|
|
Chrysamine G and its derivative reduce amyloid beta-induced neurotoxicity in mice.
Neurosci. Lett. 333 , 5-8, (2002) The neurotoxicity of amyloid beta (Abeta) is widely believed to play a seminal role in neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. We examined the effect of Chrysamine G (CG) on such neurotoxicity using the specific measurement of surviving neurons. CG was foun... |
|
|
99mTc-MAMA-chrysamine G, a probe for beta-amyloid protein of Alzheimer's disease.
Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 26(11) , 1392-9, (1999) Chrysamine G (CG), an analogue of Congo red, is known to bind in vitro to the beta-amyloid protein (Abeta 10-43) and to homogenates of several regions of the brain of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients. We synthesised a conjugate of 2-(acetamido)-CG with a bis... |
|
|
Inhibition of polyglutamine aggregation in R6/2 HD brain slices-complex dose-response profiles.
Neurobiol. Dis. 8(6) , 1017-26, (2001) Huntington's disease (HD) is a late onset neurodegenerative disorder caused by a CAG/polyglutamine (polyQ) repeat expansion. PolyQ aggregates can be detected in the nuclei and processes of neurons in HD patients and mouse models prior to the onset of symptoms... |
|
|
In vitro drug treatments reduce the deleterious effects of aggregates containing polyAla expanded PHOX2B proteins
Neurobiol. Dis. 45 , 508-18, (2012) Heterozygous in frame duplications of the PHOX2B gene, leading to polyalanine (polyAla) expansions ranging from +5 to +13 residues of a 20-alanine stretch, have been identified in the vast majority of patients affected with Congenital Central Hypoventilation ... |
|
|
Inhibition of huntingtin fibrillogenesis by specific antibodies and small molecules: implications for Huntington's disease therapy.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97(12) , 6739-44, (2000) The accumulation of insoluble protein aggregates in intra and perinuclear inclusions is a hallmark of Huntington's disease (HD) and related glutamine-repeat disorders. A central question is whether protein aggregation plays a direct role in the pathogenesis o... |
|
|
Development of small molecule probes for the beta-amyloid protein of Alzheimer's disease.
Neurobiol. Aging 15(6) , 691-8, (1994) This study describes the synthesis and in vitro testing of small molecule probes that may eventually prove useful as markers of amyloid deposition in living patients. The prototype agent, Chrysamine G (CG), is a derivative of Congo red. CG binds synthetic bet... |
|
|
Curcumin inhibits formation of amyloid beta oligomers and fibrils, binds plaques, and reduces amyloid in vivo.
J. Biol. Chem. 280(7) , 5892-901, (2005) Alzheimer's disease (AD) involves amyloid beta (Abeta) accumulation, oxidative damage, and inflammation, and risk is reduced with increased antioxidant and anti-inflammatory consumption. The phenolic yellow curry pigment curcumin has potent anti-inflammatory ... |
|
|
Chrysamine-G binding to Alzheimer and control brain: autopsy study of a new amyloid probe.
Neurobiol. Aging 16(4) , 541-8, (1995) Chrysamine-G (CG) is a carboxylic acid analogue of Congo red, a histologic dye which stains amyloid. CG binds to the beta-amyloid protein of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in vitro and partitions into the brain of normal mice. In this study, we demonstrate increase... |