Chrysamine G and its derivative reduce amyloid beta-induced neurotoxicity in mice.
Kazuhiro Ishii, William E Klunk, Shigeki Arawaka, Manik L Debnath, Yoshiko Furiya, Naruhiko Sahara, Shin'ichi Shoji, Akira Tamaoka, Jay W Pettegrew, Hiroshi Mori
文献索引:Neurosci. Lett. 333 , 5-8, (2002)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The neurotoxicity of amyloid beta (Abeta) is widely believed to play a seminal role in neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. We examined the effect of Chrysamine G (CG) on such neurotoxicity using the specific measurement of surviving neurons. CG was found to reduce the neurodegeneration induced by both the active short fragment of Abeta(25-35) and full-sized Abeta(1-40). In this study, we synthesized a new chemical compound from a monovalent structure of CG (hCG), with a lower affinity for Abeta, and compared its activity with that of CG. Both CG and hCG were found to be equally efficacious in reducing Abeta-induced neuronal death at a concentration of 0.1-1 microM, indicating that the mechanism of action for CG was not due to its chelating activity, but rather due to its anti-oxidant activity.Copyright 2002 Elsevier Science Ireland Ltd.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
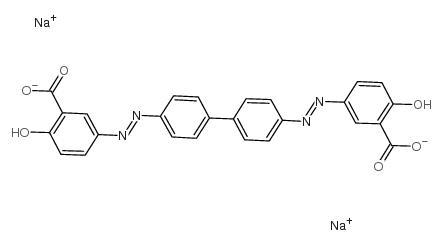 |
N-芴甲氧羰基-D-1,2,3,4-四氢异喹啉-3-羧酸
CAS:6472-91-9 |
C26H16N4Na2O6 |
|
Imaging Abeta plaques in living transgenic mice with multiph...
2002-09-01 [J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 61 , 797-805, (2002)] |
|
Amyloid binding ligands as Alzheimer's disease therapies.
2002-01-01 [Neurobiol. Aging 23 , 1039-1042, (2002)] |
|
99mTc-MAMA-chrysamine G, a probe for beta-amyloid protein of...
1999-11-01 [Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 26(11) , 1392-9, (1999)] |
|
Inhibition of polyglutamine aggregation in R6/2 HD brain sli...
2001-12-01 [Neurobiol. Dis. 8(6) , 1017-26, (2001)] |
|
In vitro drug treatments reduce the deleterious effects of a...
2012-01-01 [Neurobiol. Dis. 45 , 508-18, (2012)] |