植烷酸
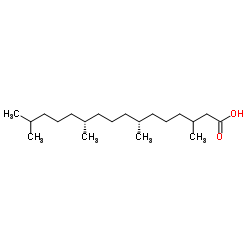
植烷酸结构式

|
常用名 | 植烷酸 | 英文名 | Phytanic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 14721-66-5 | 分子量 | 312.530 | |
| 密度 | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 422.3±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C20H40O2 | 熔点 | -65°C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 179.7±11.2 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Phytanic acid and very long chain fatty acids in genetic peroxisomal disorders.
J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 27(5) , 309-14, (1989) 1. Phytanic acid, phytanyl-triacylglycerols, and very long chain fatty acids were analysed by gas chromatography or thin-layer chromatography in blood and tissues of patients with different genetic peroxisomal disorders (Refsum's disease, X-linked adrenoleuko... |
|
|
Polyunsaturated Branched-Chain Fatty Acid Geranylgeranoic Acid Induces Unfolded Protein Response in Human Hepatoma Cells.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0132761, (2015) The acyclic diterpenoid acid geranylgeranoic acid (GGA) has been reported to induce autophagic cell death in several human hepatoma-derived cell lines; however, the molecular mechanism for this remains unknown. In the present study, several diterpenoids were ... |
|
|
New insights into the peroxisomal protein inventory: Acyl-CoA oxidases and -dehydrogenases are an ancient feature of peroxisomes.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1853(1) , 111-25, (2014) Peroxisomes are ubiquitous organelles which participate in a variety of essential biochemical pathways. An intimate interrelationship between peroxisomes and mitochondria is emerging in mammals, where both organelles cooperate in fatty acid β-oxidation and ce... |
|
|
The human liver fatty acid binding protein T94A variant alters the structure, stability, and interaction with fibrates.
Biochemistry 52(51) , 9347-57, (2013) Although the human liver fatty acid binding protein (L-FABP) T94A variant arises from the most commonly occurring single-nucleotide polymorphism in the entire FABP family, there is a complete lack of understanding regarding the role of this polymorphism in hu... |
|
|
Peroxisomal bifunctional enzyme deficiency.
J. Clin. Invest. 83(3) , 771-7, (1989) Peroxisomal function was evaluated in a male infant with clinical features of neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy. Very long chain fatty acid levels were elevated in both plasma and fibroblasts, and beta-oxidation of very long chain fatty acids in cultured fibrobla... |
|
|
Phytanic acid induces Neuro2a cell death via histone deacetylase activation and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 48 , 33-9, (2015) Phytanic acid is a branched fatty acid that is a metabolic intermediate of chlorophyll. In this study, the effects of phytanic acid on Histone deacetylase (Hdac) activity were examined in an in vitro enzyme assay and in neuronal Neuro2a cells. Several fatty a... |
|
|
2,6-Dimethyloctanedioic acid--a metabolite of phytanic acid in Refsum's disease.
Clin. Chem. 29(3) , 434-7, (1983) The urine of two patients with Refsum's disease consistently contained 2,6-dimethyloctanedioic acid, a compound not normally found in human urine. In addition, their urines contained increased concentrations of 3-methylhexanedioic acid. These two compounds ma... |
|
|
Metabolism of phytanic acid and 3-methyl-adipic acid excretion in patients with adult Refsum disease.
J. Lipid Res. 44(8) , 1481-8, (2003) Adult Refsum disease (ARD) is associated with defective alpha-oxidation of phytanic acid (PA). omega-Oxidation of PA to 3-methyl-adipic acid (3-MAA) occurs although its clinical significance is unclear. In a 40 day study of a new ARD patient, where the plasma... |
|
|
Infantile Refsum's disease: biochemical findings suggesting multiple peroxisomal dysfunction.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 9(2) , 169-74, (1986) Infantile Refsum's disease was diagnosed in three male patients, presenting with facial dysmorphia, retinitis pigmentosa, neurosensory hearing loss, hepatomegaly, osteopenia and delayed growth and psychomotor development. An elevated plasma phytanic acid conc... |
|
|
Phytanic acid stimulates glucose uptake in a model of skeletal muscles, the primary porcine myotubes.
Lipids Health Dis. 12 , 14, (2013) Phytanic acid (PA) is a chlorophyll metabolite with potentials in regulating glucose metabolism, as it is a natural ligand of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) that is known to regulate hepatic glucose homeostasis. This study aimed to esta... |