4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
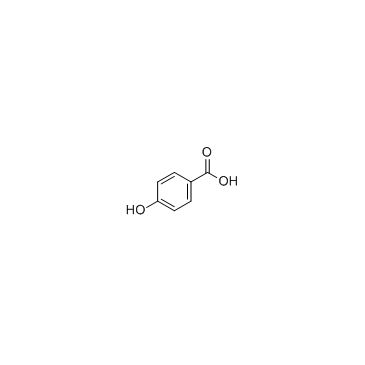
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 99-96-7 | Molecular Weight | 138.121 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 336.2±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O3 | Melting Point | 213-217 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 171.3±19.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid, could inhibit most gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria, with an IC50 of 160 μg/mL. |
| Name | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid, could inhibit most gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria, with an IC50 of 160 μg/mL. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite Bacteria:160 μg/mL (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Most of the gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria are sensitive to trans 4-Hydroxycinnamic acid (4-HBA) and 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid at IC50 concentrations of 100-170 and 160 μg/mL, respectively. The antimicrobial activities of 4-Hydroxycinnamic acid and t4-HCA against 11 food pathogenic bacteria, 6 plant pathogenic bacteria, 2 yeasts and 15 plant pathogenic fungi are tested by the paper disc method. These compounds inhibit the growth of most of the bacteria and yeasts at concentrations of 200-400 μg. However, the inhibition is more effective against most of the gram-positive bacteria. When tested by the paper disc method, 4-Hydroxycinnamic acid has stronger antimicrobial activity than t4-HCA against S. aureus, L. mesenteroides, S. cerevisiae and C. albicans at a concentration of 50 μg. However, no inhibitory effect against fungi was observed at concentrations even up to 1000 μg[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 336.2±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 213-217 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 138.121 |
| Flash Point | 171.3±19.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 138.031693 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 1.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.616 |
| InChIKey | FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)c1ccc(O)cc1 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Water Solubility | 5 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | DH1925000 |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918290000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2918290000 other carboxylic acids with phenol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) VAT:17.0% MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Comparison between ATR-IR, Raman, concatenated ATR-IR and Raman spectroscopy for the determination of total antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content of Chinese rice wine.
Food Chem. 194 , 671-9, (2015) The application of attenuated total reflectance infrared spectroscopy (ATR-IR), Raman spectroscopy (RS) and combination of ATR-IR and RS for measurements of total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and total ... |
|
|
Arhodomonas sp. strain Seminole and its genetic potential to degrade aromatic compounds under high-salinity conditions.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80(21) , 6664-76, (2014) Arhodomonas sp. strain Seminole was isolated from a crude oil-impacted brine soil and shown to degrade benzene, toluene, phenol, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (4-HBA), protocatechuic acid (PCA), and phenylace... |
|
|
Antagonistic control of a dual-input mammalian gene switch by food additives.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(14) , e116, (2014) Synthetic biology has significantly advanced the design of mammalian trigger-inducible transgene-control devices that are able to programme complex cellular behaviour. Fruit-based benzoate derivatives... |
| 4-Hydroxybenzoicacid |
| Benzoic acid,4-hydroxy |
| PARAHYDROXY BENZOIC ACID |
| MFCD00002547 |
| EINECS 202-804-9 |
| 4-HYDROXYBENZOIC ACID FOR SYNTHESIS |
| 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
| p-Salicylic acid |
| 4-Hydroxy benzoic acid |
| HYDROXYBENZOIC ACID, P- POLYMER GRADE |
| |p|-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
| 4-Hydroxybenzoesaeure |
| Benzoic acid,p-hydroxy |
| P-HYDROXYBENZOIC ACID, REAGENT |
| PROPYL PARAHYDROXYBENZOATE IMP. A (EP): 4-HYDROXYBENZOIC ACID, CRM STANDARD |
| ACETYLSALICYLIC ACID IMPURITY A (ASPIRIN IMPURITY A) |
| 1-Naphthyl phsophoric acid sodium salt |
| 4-Carboxyphenol |
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
| para-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
| 4-hydroxy-benzoic acid |
| papa-hydroxy-benzoic acid |
| p-carboxyphenol |
 CAS#:623-05-2
CAS#:623-05-2 CAS#:586-76-5
CAS#:586-76-5 CAS#:619-58-9
CAS#:619-58-9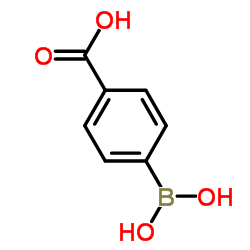 CAS#:14047-29-1
CAS#:14047-29-1 CAS#:1927-95-3
CAS#:1927-95-3 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9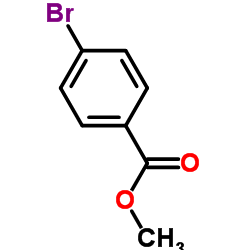 CAS#:619-42-1
CAS#:619-42-1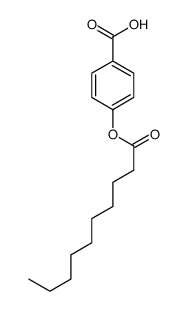 CAS#:86960-46-5
CAS#:86960-46-5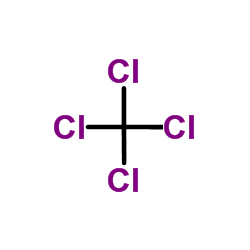 CAS#:56-23-5
CAS#:56-23-5 CAS#:108-95-2
CAS#:108-95-2 CAS#:110929-34-5
CAS#:110929-34-5![6,8-dibromo-2-methyl-3-[[2-(4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)-3H-1,3,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]methyl]quinazolin-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/378/106924-13-4.png) CAS#:106924-13-4
CAS#:106924-13-4 CAS#:111833-05-7
CAS#:111833-05-7![2-methyl-3-[[2-(4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)-3H-1,3,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]methyl]quinazolin-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/471/106924-06-5.png) CAS#:106924-06-5
CAS#:106924-06-5 CAS#:1076199-77-3
CAS#:1076199-77-3![5-hydroxy-2-[(4-hydroxybenzoyl)amino]benzoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/440/110846-17-8.png) CAS#:110846-17-8
CAS#:110846-17-8 CAS#:111973-84-3
CAS#:111973-84-3 CAS#:106047-17-0
CAS#:106047-17-0 CAS#:5216-25-1
CAS#:5216-25-1 CAS#:104-93-8
CAS#:104-93-8
