DL-Norvaline
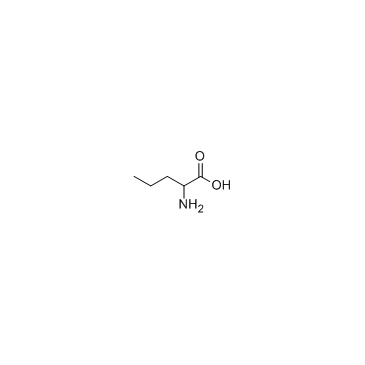
DL-Norvaline structure
|
Common Name | DL-Norvaline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 760-78-1 | Molecular Weight | 117.146 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 222.9±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2 | Melting Point | ≥300 °C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 88.6±22.6 °C | |
Use of DL-NorvalineDL-Norvaline, a derivative of L-norvaline, L-norvaline is a non-competitive inhibitor of arginase. |
| Name | 2-aminopentanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DL-Norvaline, a derivative of L-norvaline, L-norvaline is a non-competitive inhibitor of arginase. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | DL-Norvaline, a derivative of L-norvaline[1], L-norvaline is a non-competitive inhibitor of arginase[2]. |
| Cell Assay | A murine macrophage cell line (RAW264.7) is used throughout the study, RAW264.7 cells are induced by A. actinomycetemcomitans-lipopolysaccharide, cells are incubated with various concentrations of L-norvaline or DL-norvaline (0.01, 0.1, 1, 10 mM) and 10 μg of A. actinomycetemcomitans-lipopolysaccharide. In other experiments, cells are incubated with antimurine CD14 or antimurine toll-like receptor 2 and 4 antibody at room temperature for 1 h, washed three times, and then stimulated with 10 μg of A. actinomycetemcomitans-lipopolysaccharide. All experiments are repeated three times, each consisting of triplicate cultures[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 222.9±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | ≥300 °C (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 117.146 |
| Flash Point | 88.6±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 117.078979 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | 0.38 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.464 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Water Solubility | 1 g/10 mL (18 ºC) |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29224995 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 29224995 |
|---|
|
Mouse hepatocytes and LSEC proteome reveal novel mechanisms of ischemia/reperfusion damage and protection by A2aR stimulation.
J. Hepatol. 62(3) , 573-80, (2015) Ischemia-reperfusion (IR) of liver results in hepatocytes (HP) and sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSEC) irreversible damage. Ischemic preconditioning protects IR damage upon adenosine A2a receptor (A2a... |
|
|
Analysis of beers from an 1840s' shipwreck.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63(9) , 2525-36, (2015) Two bottles of beer from an about 170-year-old shipwreck (M1 Fö 403.3) near the Åland Islands in the Baltic Sea were analyzed. Hop components and their degradation compounds showed that the bottles co... |
|
|
Teicoplanin bonded sub-2 μm superficially porous particles for enantioseparation of native amino acids.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 114 , 247-53, (2015) Superficially porous particles (SPPs) demonstrate superior efficiency than totally porous particles in chiral separations. In order to obtain high efficiency and fast separation, sub-2 μm SPPs with hi... |
| DL-NORVALINE |
| α-DL-Aminopentanoic acid |
| DL-2-Aminovaleric Acid |
| 2-Aminovaleric acid |
| MFCD00064420 |
| DL-norVal-OH |
| DL-2-Aminopentanoic acid |
| (±)-2-Aminopentanoic acid |
| H-DL-Nva-OH |
| rac-norvaline |
| a-Aminovaleric Acid |
| 2-Aminopentanoic acid |
| EINECS 212-082-7 |
| APE |
| DL-α-Aminovaleric acid |
| Norvaline |
| Norvaline, DL- |
| NVA |
| UNII:V639KTF2SZ |
| Norvaline (VAN) |
| (±)-Norvaline |
| aminovaleric acid |
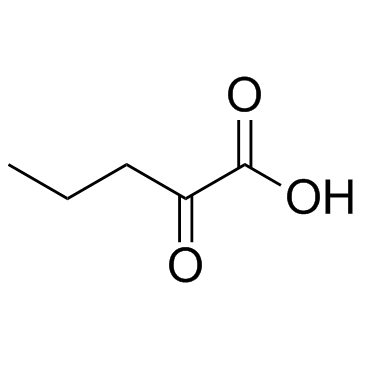 CAS#:1821-02-9
CAS#:1821-02-9 CAS#:56548-09-5
CAS#:56548-09-5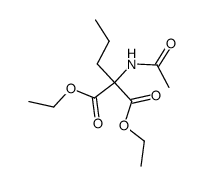 CAS#:82518-89-6
CAS#:82518-89-6 CAS#:6967-47-1
CAS#:6967-47-1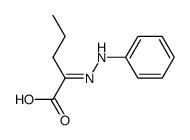 CAS#:64527-14-6
CAS#:64527-14-6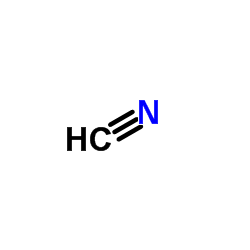 CAS#:74-90-8
CAS#:74-90-8 CAS#:40898-95-1
CAS#:40898-95-1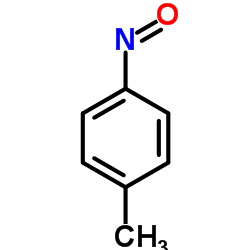 CAS#:623-11-0
CAS#:623-11-0 CAS#:7647-01-0
CAS#:7647-01-0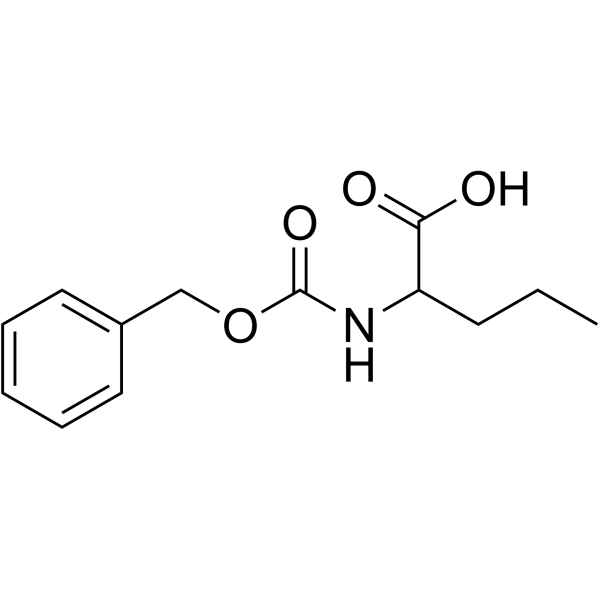 CAS#:21691-43-0
CAS#:21691-43-0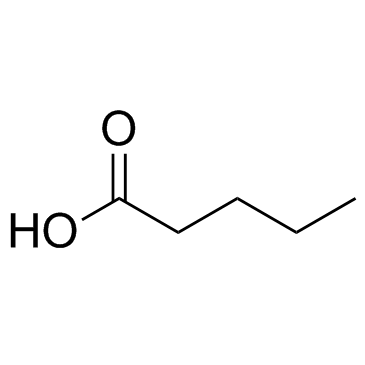 CAS#:109-52-4
CAS#:109-52-4 CAS#:7682-15-7
CAS#:7682-15-7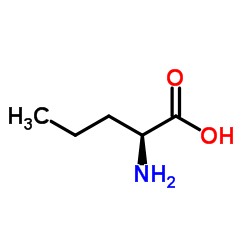 CAS#:6600-40-4
CAS#:6600-40-4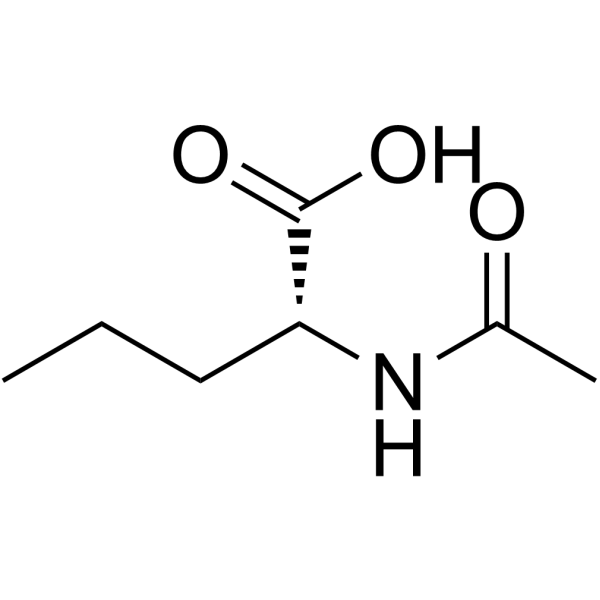 CAS#:57357-56-9
CAS#:57357-56-9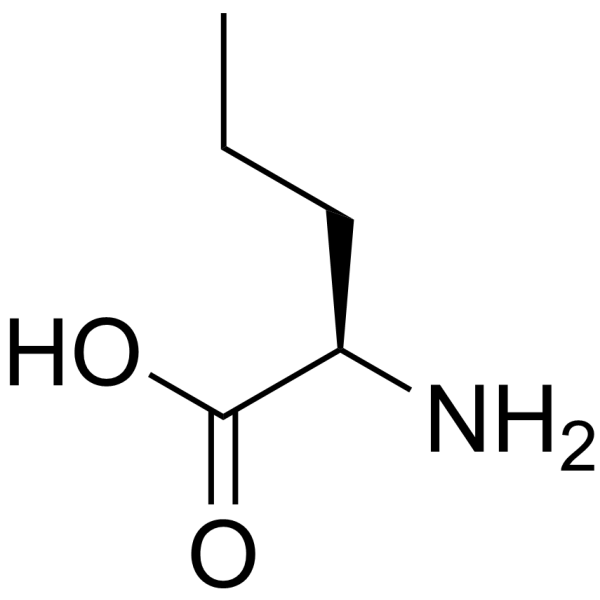 CAS#:2013-12-9
CAS#:2013-12-9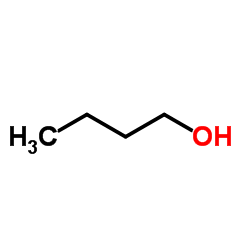 CAS#:71-36-3
CAS#:71-36-3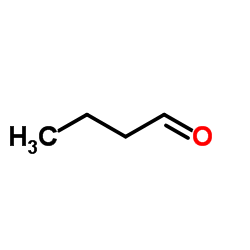 CAS#:123-72-8
CAS#:123-72-8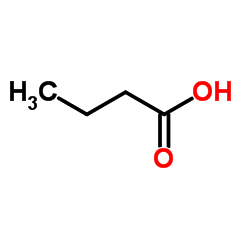 CAS#:107-92-6
CAS#:107-92-6
