Bupivacaine Hydrochloride
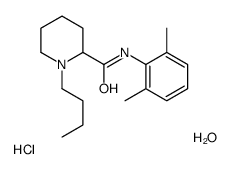
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Bupivacaine Hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 73360-54-0 | Molecular Weight | 342.90 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H31ClN2O2 | Melting Point | 255-259℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Bupivacaine HydrochlorideBupivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate is a NMDA receptor inhibitor. Bupivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate can block sodium, L-calcium, and potassium channels. Bupivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate potently blocks SCN5A channels with the IC50 of 69.5 μM. Bupivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate can be used for the research of chronic pain[1][2][3]. |
| Name | bupivacaine hydrochloride hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Bupivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate is a NMDA receptor inhibitor. Bupivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate can block sodium, L-calcium, and potassium channels. Bupivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate potently blocks SCN5A channels with the IC50 of 69.5 μM. Bupivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate can be used for the research of chronic pain[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
NMDA Receptor |
| References |
| Melting Point | 255-259℃ |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H31ClN2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 342.90 |
| Exact Mass | 342.20700 |
| PSA | 45.06000 |
| LogP | 5.22160 |
| InChIKey | HUCIWBPMHXGLFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCN1CCCCC1C(=O)Nc1c(C)cccc1C.Cl.O |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300 + H310 + H330 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P280-P284-P301 + P310-P302 + P350 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
| Risk Phrases | 26/27/28 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1 / PGII |
| RTECS | TK6125000 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
|
Differential requirement for IL-2 and IL-15 during bifurcated development of thymic regulatory T cells.
J. Immunol. 193(11) , 5525-33, (2014) The developmental pathways of regulatory T cells (T(reg)) generation in the thymus are not fully understood. In this study, we reconstituted thymic development of Zap70-deficient thymocytes with a tet... |
|
|
The distinct effects of lipid emulsions used for "lipid resuscitation" on gating and bupivacaine-induced inhibition of the cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5.
Anesth. Analg. 117(5) , 1101-8, (2013) Systemic administration of lipid emulsions is an established treatment for local anesthetic intoxication. However, it is unclear by which mechanisms lipids achieve this function. The high cardiac toxi... |
|
|
MK-801-induced behavioural sensitisation alters dopamine release and turnover in rat prefrontal cortex.
Psychopharmacol. Ser. 232(3) , 509-17, (2015) Repeated exposure to psychostimulants that either increase dopamine (DA) release or target N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors can induce behavioural sensitisation, a phenomenon that may be importan... |
| Win 11,318 |
| Bupivacaine HCl H2-O |
| 1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide hydrate hydrochloride |
| Bupivacaine hydrochloride |
| Marcaine (TN) |
| 1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide,hydrate,hydrochloride |
| 2-Piperidinecarboxamide,1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-,monohydrochloride,monohydrate |