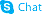Kainic acid hydrate

Kainic acid hydrate structure
|
Common Name | Kainic acid hydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 58002-62-3 | Molecular Weight | 213.230 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 439.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H15NO4 | Melting Point | 250-252°C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 219.8±28.7 °C | |
Use of Kainic acid hydrateKainic acid hydrate is a potent excitotoxic agent. Kainic acid hydrate also is an agonist for a subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptor. Kainic acid hydrate induces seizures[1][2]. |
| Name | (−)-(α)-Kainic Acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Kainic acid hydrate is a potent excitotoxic agent. Kainic acid hydrate also is an agonist for a subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptor. Kainic acid hydrate induces seizures[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Kainic acid hydrate (5 mg/kg;腹腔注射;每小时一次至少 3 小时,直至癫痫持续状态) 诱导大鼠癫痫发作[1]。 Animal Model: 8 weeks, 200-250 g male adult Wistar rats[1] Dosage: 5 mg/kg Administration: I.p.; hourly at least 3 h until status epilepticus Result: Induced seizures in rats. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 439.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 250-252°C |
| Molecular Formula | C10H15NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 213.230 |
| Flash Point | 219.8±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 213.100113 |
| LogP | 0.50 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.509 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22;S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
MicroRNA-124 and -137 cooperativity controls caspase-3 activity through BCL2L13 in hippocampal neural stem cells.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 12448, (2015) Adult neurogenesis continuously contributes new neurons to hippocampal circuits and the programmed death of a subset of immature cells provides a primary mechanism controlling this contribution. Epile... |
|
|
Nodule excitability in an animal model of periventricular nodular heterotopia: c-fos activation in organotypic hippocampal slices.
Epilepsia 56(4) , 626-35, (2015) Aberrations in brain development may lead to dysplastic structures such as periventricular nodules. Although these abnormal collections of neurons are often associated with difficult-to-control seizur... |
|
|
Plasticity of calcium signaling cascades in human embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors.
Stem Cells Dev. 22(10) , 1506-21, (2013) Human embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors (hESC NPs) are considered to be a promising tool for cell-based therapy in central nervous system injuries and neurodegenerative diseases. The Ca(2+... |
| kainic acid |
| MFCD00150833 |
| (3S,4S)-3-(Carboxymethyl)-4-isopropenyl-L-proline |
| (−)-Kainic Acid |
| L-Proline, 3-(carboxymethyl)-4-(1-methylethenyl)-, (3S,4S)- |