DL-Glyceric aldehyde
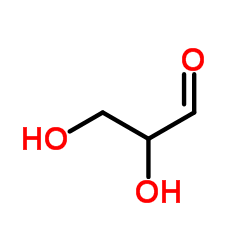
DL-Glyceric aldehyde structure
|
Common Name | DL-Glyceric aldehyde | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56-82-6 | Molecular Weight | 90.08 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 228.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O3 | Melting Point | 144-145ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 106.0±14.7 °C | |
Use of DL-Glyceric aldehydeDL-Glyceraldehyde is a monosaccharide. DL-Glyceraldehyde is the simplest aldose. DL-Glyceraldehyde can be used for various biochemical studies[1]. |
| Name | h-pro-asn-oh |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DL-Glyceraldehyde is a monosaccharide. DL-Glyceraldehyde is the simplest aldose. DL-Glyceraldehyde can be used for various biochemical studies[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 228.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 144-145ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 90.08 |
| Flash Point | 106.0±14.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 90.031693 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | -1.59 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.454 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | Very soluble (1000 g/L) (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MA6475000 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Vegetables' juice influences polyol pathway by multiple mechanisms in favour of reducing development of oxidative stress and resultant diabetic complications.
Pharmacogn. Mag. 10(Suppl 2) , S383-91, (2014) Hyperglycemia induced generation of free radicals and consequent development of oxidative stress by polyol pathway is one of the crucial mechanisms stirring up development of diabetic complications. W... |
|
|
Fungal metabolite nigerloxin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy and gentamicin-induced renal oxidative stress in experimental rats.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 387(9) , 849-59, (2014) Elevated polyol pathway enzyme activities and oxidative stress play an important role in the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy. Here, we investigated the beneficial influence of nige... |
|
|
Triosephosphate isomerase of Taenia solium (TTPI): phage display and antibodies as tools for finding target regions to inhibit catalytic activity.
Parasitol. Res. 114(1) , 55-64, (2015) Previous studies demonstrated that antibodies against triosephosphate isomerase of Taenia solium (TTPI) can alter its enzymatic catalysis. In the present study, we used antibodies produced against the... |
| a,b-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde |
| EINECS 200-290-0 |
| DL-Glyceraldehyde |
| Glyceraldehyde, (±)- |
| potassium DL-glutamate monohydrate |
| (±)-glyceraldehyde |
| 2,3-Dihydroxypropanal |
| Glyceraldehyde |
| Propanal, 2,3-dihydroxy- |
| glycerose |
| DL-glutamic acid,dipotassium-salt |
| Mannuronic acid |
| α,β-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde |
| DL-Glutaminsaeure,Dikalium-Salz |
| (±)-2,3-dihydroxy-Propanal |
| MFCD00064379 |
| DL-Glyceric aldehyde |
 CAS#:56-81-5
CAS#:56-81-5 CAS#:50-00-0
CAS#:50-00-0 CAS#:57-50-1
CAS#:57-50-1 CAS#:50-99-7
CAS#:50-99-7 CAS#:57-48-7
CAS#:57-48-7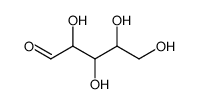 CAS#:53106-52-8
CAS#:53106-52-8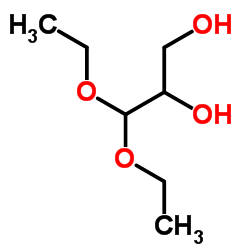 CAS#:10487-05-5
CAS#:10487-05-5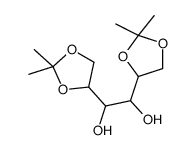 CAS#:53735-98-1
CAS#:53735-98-1 CAS#:64-18-6
CAS#:64-18-6 CAS#:107-02-8
CAS#:107-02-8 CAS#:551-84-8
CAS#:551-84-8 CAS#:95-43-2
CAS#:95-43-2 CAS#:10323-20-3
CAS#:10323-20-3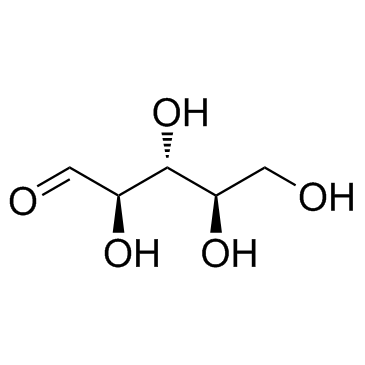 CAS#:50-69-1
CAS#:50-69-1 CAS#:1114-34-7
CAS#:1114-34-7 CAS#:473-81-4
CAS#:473-81-4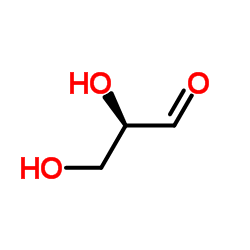 CAS#:453-17-8
CAS#:453-17-8 CAS#:497-09-6
CAS#:497-09-6 CAS#:19456-80-5
CAS#:19456-80-5
