3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid
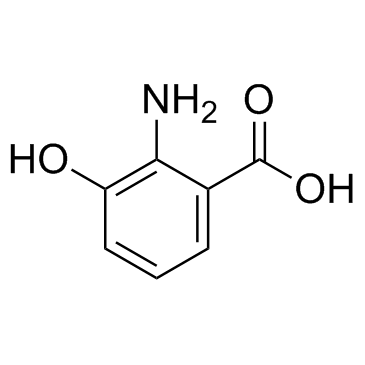
3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid structure
|
Common Name | 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 548-93-6 | Molecular Weight | 153.135 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 356.9±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H7NO3 | Melting Point | 240 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 169.6±26.5 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid is a tryptophan metabolite in the kynurenine pathway. |
| Name | 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid is a tryptophan metabolite in the kynurenine pathway. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 356.9±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 240 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H7NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 153.135 |
| Flash Point | 169.6±26.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 153.042587 |
| PSA | 83.55000 |
| LogP | 1.05 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.691 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 + H332-H315-H319-H335-H351 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 20/21/22-36/37/38-40 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DG2625000 |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Increased conversion of tryptophan to nicotinamide in rats by dietary valproate.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 77(2) , 295-300, (2013) Valproic acid (VPA) is a short-chained, branched fatty acid that is widely used in humans as an anticonvulsant and mood stabilizer, and has been reported to increase the liver NAD concentration. We in... |
|
|
Time-dependent effects of L-tryptophan administration on urinary excretion of L-tryptophan metabolites.
J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 60(4) , 255-60, (2014) We have previously reported that dietary supplementation with up to 5.0 g/d of L-tryptophan (L-Trp) for 21 d has no adverse effects, judging from the levels of general blood variables, in healthy wome... |
|
|
The niacin required for optimum growth can be synthesized from L-tryptophan in growing mice lacking tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase.
J. Nutr. 143(7) , 1046-51, (2013) In mammals, nicotinamide (Nam) is biosynthesized from l-tryptophan (l-Trp). The enzymes involved in the initial step of the l-Trp→Nam pathway are l-Trp-2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) and indoleamine-2,3-dioxyg... |
| Acid, 3-Hydroxyanthranilic |
| MFCD00007700 |
| 3-hydroxy-Anthranilic acid |
| Anthranilic acid, 3-hydroxy- |
| 3-Hydroxy-2-aminobenzoic acid |
| 3-OH-anthranilic acid |
| EINECS 208-962-5 |
| Benzoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy- |
| 2-Amino-3-hydroxybenzoic acid |
| 3-Hydroxy-2-aminobenzoate |
 CAS#:63478-14-8
CAS#:63478-14-8 CAS#:4920-80-3
CAS#:4920-80-3 CAS#:3177-80-8
CAS#:3177-80-8 CAS#:602-00-6
CAS#:602-00-6 CAS#:606-59-7
CAS#:606-59-7 CAS#:73453-77-7
CAS#:73453-77-7 CAS#:54002-28-7
CAS#:54002-28-7 CAS#:135891-44-0
CAS#:135891-44-0 CAS#:37114-03-7
CAS#:37114-03-7 CAS#:146-90-7
CAS#:146-90-7![Benzo[d]oxazole-4-carboxylic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/109/208772-23-0.png) CAS#:208772-23-0
CAS#:208772-23-0 CAS#:59-67-6
CAS#:59-67-6 CAS#:89-00-9
CAS#:89-00-9 CAS#:128156-54-7
CAS#:128156-54-7 CAS#:128156-55-8
CAS#:128156-55-8 CAS#:136497-59-1
CAS#:136497-59-1![6-amino-3-[(2-carboxy-6-hydroxyphenyl)amino]-2,5-dioxo-1,3-cyclohexadiene-1-carboxylic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/010/112817-49-9.png) CAS#:112817-49-9
CAS#:112817-49-9
