Aloeemodin
Aloeemodin structure
|
Common Name | Aloeemodin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 481-72-1 | Molecular Weight | 270.237 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 568.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O5 | Melting Point | 223-224°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 311.9±26.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of AloeemodinAloe emodin is a hydroxyanthraquinone present in Aloe vera leaves, has a specific in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity.IC50 value:Target:in vitro: aloe-emodin treatment led to the dissociation of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) and ER α and increased ER α ubiquitination. Protein fractionation results suggest that aloe-emodin tended to induce cytosolic ER α degradation [1]. Aloe-emodin, a natural compound found in aloe, inhibited both proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of PC3 cells. Protein content analysis suggested that activation of the downstream substrates of mTORC2, Akt and PKCα, was inhibited by aloe-emodin treatment. Pull-down assay and in vitro kinase assay results indicated that aloe-emodin could bind with mTORC2 in cells and inhibit its kinase activity [2]. Of three anthraquinone derivatives, aloe-emodin, with a lower cytotoxicity showed concentration-dependently reducing virus-induced cytopathic effect and inhibiting replication of influenza A in MDCK cells. Galectin-3 also inhibited influenza A virus replication. Proteomic analysis of treated cells indicated galectin-3 up-regulation as one anti-influenza A virus action by aloe-emodin. Since galectin-3 exhibited cytokine-like regulatory actions via JAK/STAT pathways, aloe-emodin also restored NS1-inhibited STAT1-mediated antiviral responses in transfected cells: e.g., STAT1 phosphorylation of interferon (IFN) stimulation response element (ISRE)-driven promoter, RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) and 2'5',-oligoadenylate synthetase (2'5',-OAS) expression [3]. AE downregulated mRNA expression and promoter/gelatinolytic activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2/9, as well as the RhoB expression at gene and protein level. AE suppressed the nuclear translocation and DNA binding of NF-κB [4].in vivo: Aloe-emodin also exhibited tumor suppression effects in vivo in an athymic nude mouse model [2]. |
| Name | Aloe emodin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Aloe emodin is a hydroxyanthraquinone present in Aloe vera leaves, has a specific in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity.IC50 value:Target:in vitro: aloe-emodin treatment led to the dissociation of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) and ER α and increased ER α ubiquitination. Protein fractionation results suggest that aloe-emodin tended to induce cytosolic ER α degradation [1]. Aloe-emodin, a natural compound found in aloe, inhibited both proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of PC3 cells. Protein content analysis suggested that activation of the downstream substrates of mTORC2, Akt and PKCα, was inhibited by aloe-emodin treatment. Pull-down assay and in vitro kinase assay results indicated that aloe-emodin could bind with mTORC2 in cells and inhibit its kinase activity [2]. Of three anthraquinone derivatives, aloe-emodin, with a lower cytotoxicity showed concentration-dependently reducing virus-induced cytopathic effect and inhibiting replication of influenza A in MDCK cells. Galectin-3 also inhibited influenza A virus replication. Proteomic analysis of treated cells indicated galectin-3 up-regulation as one anti-influenza A virus action by aloe-emodin. Since galectin-3 exhibited cytokine-like regulatory actions via JAK/STAT pathways, aloe-emodin also restored NS1-inhibited STAT1-mediated antiviral responses in transfected cells: e.g., STAT1 phosphorylation of interferon (IFN) stimulation response element (ISRE)-driven promoter, RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) and 2'5',-oligoadenylate synthetase (2'5',-OAS) expression [3]. AE downregulated mRNA expression and promoter/gelatinolytic activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2/9, as well as the RhoB expression at gene and protein level. AE suppressed the nuclear translocation and DNA binding of NF-κB [4].in vivo: Aloe-emodin also exhibited tumor suppression effects in vivo in an athymic nude mouse model [2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 568.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 223-224°C |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 270.237 |
| Flash Point | 311.9±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 270.052826 |
| PSA | 94.83000 |
| LogP | 3.38 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.746 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Hygroscopic |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CB6712200 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Correlation between reduction potentials and inhibitions of Epstein-Barr virus activation by anthraquinone derivatives.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18 , 4106-9, (2008) As a continuation of studies using natural and synthetic products as cancer chemopreventive agents, we used cyclic voltammetry to examine the reduction-oxidation potentials of methylated emodin deriva... |
|
|
In vitro inhibition of Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation on hydroxyapatite by subinhibitory concentrations of anthraquinones.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 1541-4, (2007) We report that certain anthraquinones (AQs) reduce Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation on hydroxyapatite at concentrations below the MIC. Although AQs are known to generate reactive oxygen species,... |
|
|
High-affinity, non-nucleotide-derived competitive antagonists of platelet P2Y12 receptors.
J. Med. Chem. 52 , 3784-93, (2009) Anthraquinone derivatives related to the moderately potent, nonselective P2Y(12) receptor antagonist reactive blue 2 (6) have been synthesized and optimized with respect to P2Y(12) receptor affinity. ... |
| EINECS 207-571-7 |
| Aloe emodin |
| MFCD00017373 |
| 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)anthracen-9,10-dion |
| 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)anthraquinone |
| ALOE-EMODIN |
| Aloeemodin:9,10-Anthracenedione,1,8-dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-, |
| Aloeemodin |
| 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)anthraquinone,3-Hydroxymethylchrysazine,Aloe-emodin |
| 3-Hydroxymethylchrysazine |
| EMODINE |
| 1,8-dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)anthracene-9,10-dione |
| Rhabarberone |
| 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)anthra-9,10-quinone |
| 3-Hydroxymethylchrysazin |
| 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)anthraquinone,3-Hydroxymethylchrysazine |
| 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-9,10-anthraquinone |
| Diacerein impurity B |
| 9,10-Anthracenedione, 1,8-dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)- |
 CAS#:481-74-3
CAS#:481-74-3 CAS#:65615-58-9
CAS#:65615-58-9 CAS#:72036-12-5
CAS#:72036-12-5 CAS#:1415-73-2
CAS#:1415-73-2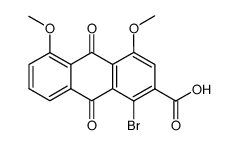 CAS#:72049-23-1
CAS#:72049-23-1 CAS#:2161-90-2
CAS#:2161-90-2 CAS#:124010-11-3
CAS#:124010-11-3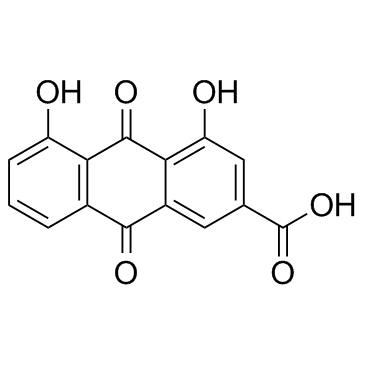 CAS#:478-43-3
CAS#:478-43-3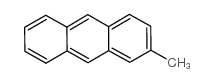 CAS#:613-12-7
CAS#:613-12-7![3-[[(2R,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3-amino-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]-1,8-dihydroxyanthracene-9,10-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/244/102831-03-8.png) CAS#:102831-03-8
CAS#:102831-03-8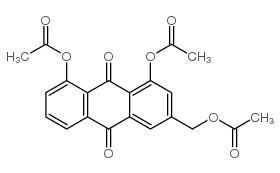 CAS#:25395-11-3
CAS#:25395-11-3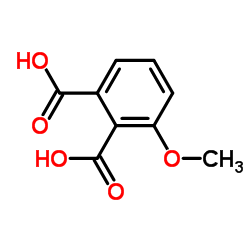 CAS#:14963-97-4
CAS#:14963-97-4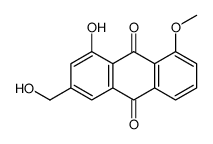 CAS#:72049-14-0
CAS#:72049-14-0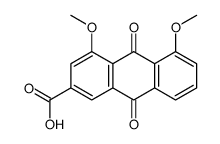 CAS#:72049-24-2
CAS#:72049-24-2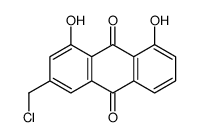 CAS#:75694-01-8
CAS#:75694-01-8
