Captopril EP Impurity C
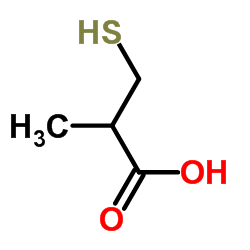
Captopril EP Impurity C structure
|
Common Name | Captopril EP Impurity C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 26473-47-2 | Molecular Weight | 120.170 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 232.5±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8O2S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 94.4±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Captopril EP Impurity CCaptopril EP Impurity C is an impurity of Captopril. Captopril (SQ-14534), antihypertensive agent, is a thiol-containing competitive, orally active angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor (IC50=0.025 μM)[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 2-methyl-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Captopril EP Impurity C is an impurity of Captopril. Captopril (SQ-14534), antihypertensive agent, is a thiol-containing competitive, orally active angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor (IC50=0.025 μM)[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 232.5±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 120.170 |
| Flash Point | 94.4±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 120.024498 |
| PSA | 76.10000 |
| LogP | 0.78 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.491 |
| InChIKey | MHRDCHHESNJQIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(CS)C(=O)O |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 5 | |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
The utilization of 3-mercapto-2-methylpropionate as sulphur source by a phototrophic bacterium.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2(7) , 589-93, (1994) A bacterium (strain photoB) photoassimilated 3-mercapto-2-methylpropionate as sole source of sulphur with methacrylate accumulating in the medium. This was thought to be the product of a sulphur-lyase... |
|
|
Bacterial taxa that limit sulfur flux from the ocean.
Science 314(5799) , 649-52, (2006) Flux of dimethylsulfide (DMS) from ocean surface waters is the predominant natural source of sulfur to the atmosphere and influences climate by aerosol formation. Marine bacterioplankton regulate sulf... |
|
|
Methylthiol:coenzyme M methyltransferase from Methanosarcina barkeri, an enzyme of methanogenesis from dimethylsulfide and methylmercaptopropionate.
J. Bacteriol. 179(22) , 6902-11, (1997) During growth on acetate, Methanosarcina barkeri expresses catabolic enzymes for other methanogenic substrates such as monomethylamine. The range of substrates used by cells grown on acetate was furth... |
| (2RS)-2-Methyl-3-sulphanylpropanoic acid 3-Mercaptoisobutyric acid |
| Captopril impurity C |
| EINECS 247-726-6 |
| Propanoic acid, 3-mercapto-2-methyl- |
| 3-sulfhydryl isobutyric acid |
| 3-mercapto-2-methylpropionic acid |
| 3-mercapto-2-methylpropanoic acid |
| 3-Mercaptoisobutyric acid |
| MFCD00671555 |
| UNII:V3E4016VAS |
| 3-Mercapto-2-methyl propanoic acid |
| 2-Methyl-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid |
| Captopril Impurity 3 |
 CAS#:79-41-4
CAS#:79-41-4 CAS#:16674-04-7
CAS#:16674-04-7 CAS#:7440-66-6
CAS#:7440-66-6 CAS#:80750-11-4
CAS#:80750-11-4 CAS#:7732-18-5
CAS#:7732-18-5 CAS#:97-63-2
CAS#:97-63-2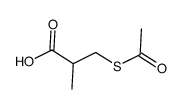 CAS#:33325-40-5
CAS#:33325-40-5 CAS#:637-51-4
CAS#:637-51-4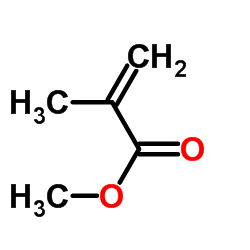 CAS#:80-62-6
CAS#:80-62-6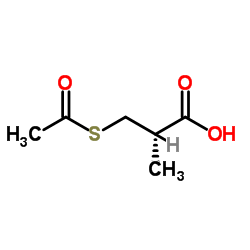 CAS#:76497-39-7
CAS#:76497-39-7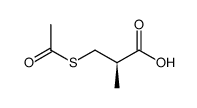 CAS#:74431-52-0
CAS#:74431-52-0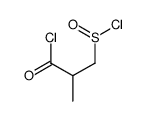 CAS#:77711-01-4
CAS#:77711-01-4 CAS#:62574-23-6
CAS#:62574-23-6 CAS#:62662-99-1
CAS#:62662-99-1