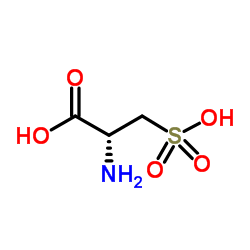
S-sulfo-L-cysteine

S-sulfo-L-cysteine structure
|
Common Name | S-sulfo-L-cysteine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1637-71-4 | Molecular Weight | 201.22100 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO5S2 | Melting Point | 184-185ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of S-sulfo-L-cysteineL-Cysteine S-sulfate is a potent N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) glutamatergic receptors agonist. L-Cysteine S-sulfate is the substrate for cystine lyase[1]. |
| Name | S-sulfo-L-cysteine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Cysteine S-sulfate is a potent N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) glutamatergic receptors agonist. L-Cysteine S-sulfate is the substrate for cystine lyase[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Melting Point | 184-185ºC |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO5S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 201.22100 |
| Exact Mass | 200.97700 |
| PSA | 151.37000 |
| LogP | 0.71540 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.604 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Stability | Store in Freezer at -20°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 20 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|
~% 
S-sulfo-L-cysteine CAS#:1637-71-4 |
| Literature: Reitz et al. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1946 , vol. 68, p. 1026,1030 |
|
~% 
S-sulfo-L-cysteine CAS#:1637-71-4 |
| Literature: Clarke Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1932 , vol. 97, p. 235,240,243,246 |
|
~% 
S-sulfo-L-cysteine CAS#:1637-71-4 |
| Literature: Uda, Narutoshi; Matoba, Yasuyuki; Kumagai, Takanori; Oda, Kosuke; Noda, Masafumi; Sugiyama, Masanori Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2013 , vol. 57, # 6 p. 2603 - 2612 |
|
~% 
S-sulfo-L-cysteine CAS#:1637-71-4 |
| Literature: Reitz et al. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1946 , vol. 68, p. 1026,1030 |
|
~% 
S-sulfo-L-cysteine CAS#:1637-71-4 |
| Literature: Micheel; Bode Chemische Berichte, 1938 , vol. 71, p. 2653,2655 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Dietary therapy in two patients with a mild form of sulphite oxidase deficiency. Evidence for clinical and biological improvement.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 23(1) , 45-53, (2000) We report an attempt at dietetic therapy in two unrelated patients with isolated sulphite oxidase deficiency, with a mild clinical course and late onset of symptoms. In case 1, disease started at 15 m... |
|
|
Urinary AASA excretion is elevated in patients with molybdenum cofactor deficiency and isolated sulphite oxidase deficiency.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 35(6) , 1031-6, (2012) Analysis of α-aminoadipic semialdehyde is an important tool in the diagnosis of antiquitin deficiency (pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy). However continuing use of this test has revealed that elevated ur... |
|
|
Molybdenum cofactor deficiency: metabolic link between taurine and S-sulfocysteine.
Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 776 , 13-9, (2013) Molybdenum cofactor deficiency (MoCD) is a rare inherited metabolic disorder characterized by severe and progressive neurologic damage mainly caused by the loss of sulfite oxidase activity. Elevated u... |
| S-Sulfocysteine |
| S-sulpho-L-cysteine |
| Cysteinyl-S-sulfonate |
| S-Sulfo-L-cystein |
| S-Sulphocysteine |
| L-Cysteine S-sulfate |
| (2R)-2-amino-3-sulfosulfanylpropanoic acid |
| Cysteine-S-sulfonate |
| S-Sulfo-L-cysteine |
| Cysteine-S-sulfate |
| Cysteinyl-S-sulfonic acid |
| MFCD00133440 |



 CAS#:498-40-8
CAS#:498-40-8
