Cinnamic acid

Cinnamic acid structure
|
Common Name | Cinnamic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 140-10-3 | Molecular Weight | 148.159 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 265.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O2 | Melting Point | 133 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 189.5±9.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Cinnamic acidtrans-Cinnamic acid is a natural antimicrobial, with minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 250 μg/mL against fish pathogen A. sobria, SY-AS1[1]. |
| Name | trans-cinnamic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | trans-Cinnamic acid is a natural antimicrobial, with minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 250 μg/mL against fish pathogen A. sobria, SY-AS1[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Bacterial[1] |
| In Vitro | trans-Cinnamic acid is an antimicrobial activity, with minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 250 μg/mL against fish pathogen A. sobria, SY-AS1. trans-cinnamic acid shows moderate inhibition on the rainbow trout intestinal isolates A. sobria SY-AS3 and S. baltica, SY-S145, gill isolate F. spartansii SY-FS1 and fish pathogens A. salmonicida ATCC 33658, Listonella anguillarum, SY-L24, V. crassostreae SY-VC10 and Y. ruckeri E42. trans-cinnamic acid is more effective on bacteria when the pH of the culture media is not neutralized[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 265.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 133 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 148.159 |
| Flash Point | 189.5±9.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 148.052429 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 2.41 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.616 |
| InChIKey | WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-VOTSOKGWSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)C=Cc1ccccc1 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Water Solubility | 0.4 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | GD7850000 |
| HS Code | 29163900 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 29163900 |
|---|
|
Analysis of initial reactions of MALDI based on chemical properties of matrixes and excitation condition.
J. Phys. Chem. B 116(32) , 9635-43, (2012) This investigation concerns the initial chemical reactions that affect the ionization of matrixes in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI). The study focuses on the relaxations of photon... |
|
|
Molecular modifications on carboxylic acid derivatives as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors: Activity and docking studies.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 5219-28, (2009) In the light of known HDAC inhibitors, 33 carboxylic acid derivatives were tested to understand the structural requirements for HDAC inhibition activity. Several modifications were applied to develop ... |
|
|
Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the synthesis of the plant polyphenol pinosylvin.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81(3) , 840-9, (2015) Plant polyphenols are of great interest for drug discovery and drug development since many of these compounds have health-promoting activities as treatments against various diseases, such as diabetes,... |
| trans-3-Phenylacrylic acid,Cinnamic acid |
| trans-Cinnamic acid |
| Cinnamic acid |
| (2E)-3-Phenylacrylic acid |
| EINECS 205-398-1 |
| MFCD00004369 |
| trans-3-Phenylacrylic Acid |
| Cinnamyl acid |
 CAS#:108-86-1
CAS#:108-86-1 CAS#:79-10-7
CAS#:79-10-7 CAS#:591-50-4
CAS#:591-50-4 CAS#:6286-30-2
CAS#:6286-30-2 CAS#:100-52-7
CAS#:100-52-7 CAS#:64-19-7
CAS#:64-19-7 CAS#:98-87-3
CAS#:98-87-3 CAS#:637-44-5
CAS#:637-44-5 CAS#:673-06-3
CAS#:673-06-3 CAS#:104-54-1
CAS#:104-54-1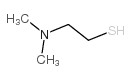 CAS#:108-02-1
CAS#:108-02-1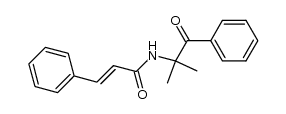 CAS#:107182-30-9
CAS#:107182-30-9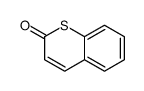 CAS#:1075-14-5
CAS#:1075-14-5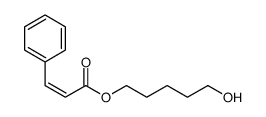 CAS#:111917-09-0
CAS#:111917-09-0 CAS#:16618-72-7
CAS#:16618-72-7 CAS#:606-83-7
CAS#:606-83-7 CAS#:614-47-1
CAS#:614-47-1 CAS#:606-86-0
CAS#:606-86-0 CAS#:356782-33-7
CAS#:356782-33-7 CAS#:538-56-7
CAS#:538-56-7
