L-Lysine, N6-formyl-
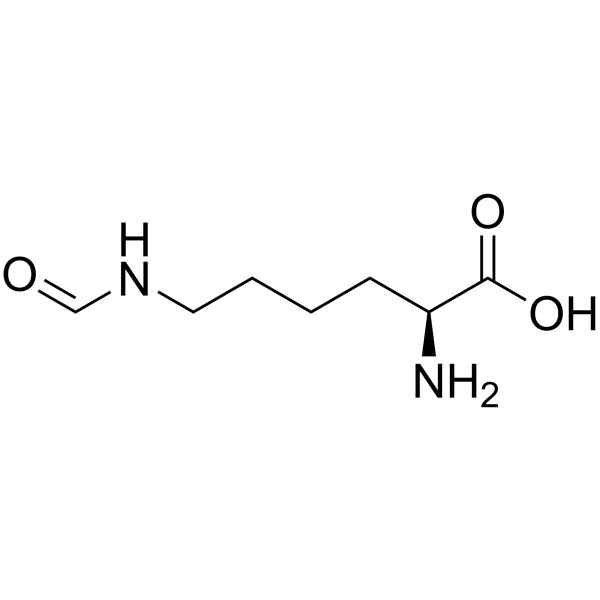
L-Lysine, N6-formyl- structure
|
Common Name | L-Lysine, N6-formyl- | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1190-48-3 | Molecular Weight | 174.19800 | |
| Density | 1.169g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 438.5ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H14N2O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 219ºC | |
Use of L-Lysine, N6-formyl-Nε-Formyl-L-lysine is a lysine derivative[1]. |
| Name | N6-formyl-L-lysine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Nε-Formyl-L-lysine is a lysine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.169g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 438.5ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C7H14N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 174.19800 |
| Flash Point | 219ºC |
| Exact Mass | 174.10000 |
| PSA | 92.42000 |
| LogP | 1.04170 |
| Vapour Pressure | 6.46E-09mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 3 ° (C=0.9, H2O) |
| InChIKey | KLPJXDPPMSJWKI-LURJTMIESA-N |
| SMILES | NC(CCCCNC=O)C(=O)O |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|
~83% 
L-Lysine, N6-formyl- CAS#:1190-48-3 |
| Literature: Akikusa; Mitsui; Sakamoto; Kikugawa Synthesis, 1992 , # 11 p. 1058 - 1060 |
|
~% 
L-Lysine, N6-formyl- CAS#:1190-48-3 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 82, p. 3727 - 3732 |
|
~% 
L-Lysine, N6-formyl- CAS#:1190-48-3 |
| Literature: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, , vol. 58, # 10 p. 6458 - 6464 |
|
~% 
L-Lysine, N6-formyl- CAS#:1190-48-3 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 42, # 12 p. 2618 - 2620 |
|
~% 
L-Lysine, N6-formyl- CAS#:1190-48-3 |
| Literature: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, , vol. 58, # 10 p. 6458 - 6464 |
|
~% 
L-Lysine, N6-formyl- CAS#:1190-48-3 |
| Literature: Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, , vol. 51, p. 1899 - 1900 |
|
~% 
L-Lysine, N6-formyl- CAS#:1190-48-3 |
| Literature: Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, , vol. 51, p. 1899 - 1900 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Analysis of glycated and ascorbylated proteins by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 50 , 5697-5703, (2002) Proteins or poly-L-lysine which were incubated in the presence of ascorbic acid, dehydroascorbic acid (ascorbylation), or various sugars (glycation) were analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectromet... |
|
|
The isolation of Nepsilon-formyl-L-lysine from the reaction between formaldehyde and L-lysine and its identification by OPLC and NMR spectroscopy.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 3 , 343-349, (1985) From the reaction between l-lysine and formaldehyde, Nepsilon-formyl-L-lysine was isolated by means of ion-exchange column chromatography. The identification of Nepsilon-formyl-L-lysine was carried ou... |
|
|
Quantitative analysis of histone modifications: formaldehyde is a source of pathological n(6)-formyllysine that is refractory to histone deacetylases.
PLoS Genet. 9(2) , e1003328, (2013) Aberrant protein modifications play an important role in the pathophysiology of many human diseases, in terms of both dysfunction of physiological modifications and the formation of pathological modif... |
| Nepsilon-ForMyl-L-lysine |
| N(6)-formyl-L-lysine |
| MFCD00037362 |
| N-ε-FORMYL-L-LYSINE |
| H-Lys(For)-OH |
| <i>N</i><sup>ε</sup>-Formyl-<small>L</small>-lysine |
| N-EPSILON-FORMYL-L-LYSINE |


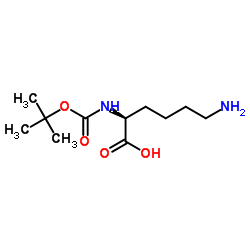
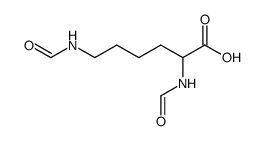
 CAS#:3105-95-1
CAS#:3105-95-1