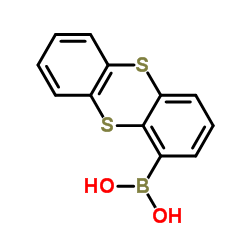
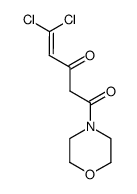
587871-26-9
| Name | 2-morpholin-4-yl-6-thianthren-1-ylpyran-4-one |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2-(4-Morpholinyl)-6-(1-thianthrenyl)-4H-pyran-4-one
2-Morpholin-4-yl-6-thianthren-1-ylpyran-4-one 2-morpholin-4-yl-6-thianthren-1-yl-pyran-4-one 2-Morpholino-6-(thianthren-1-yl)-4H-pyran-4-one KU 55933 2-Thianthren-1-yl-6-morpholin-4-yl-pyran-4-one KU55933 ATM Kinase Inhibitor KU-55933 |
| Description | KU-55933 is a potent ATM inhibitor with an IC50 and Ki of 12.9 and 2.2 nM, respectively, and is highly selective for ATM as compared to DNA-PK, PI3K/PI4K, ATR and mTOR. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
ATM:12.9 nM (IC50) DNA-PK:2500 nM (IC50) mTOR:9300 nM (IC50) PI3K:16600 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | KU-55933 (10 μM) blocks the ionizing radiation-induced p53 serine 15 phosphorylation. KU-55933 has a dose-dependent effect in inhibiting this ATM-dependent phosphorylation event with an estimated IC50 of 300 nM. KU-55933 ablates the ionizing radiation-induced phosphorylation of these ATM substrates. KU-55933 specifically inhibits ATM but not the other DNA damage-activated PIKKs, ATR, and DNA-PK[1]. KU-55933 induces pATM, p53, E2F1 and pATR, noticeably upregulates the nuclear fraction of E2F1 at the 0.5 h time point[2]. Metformin increases ATM and AMPK phosphorylation, as well as SHP protein level in primary hepatocytes, and this stimulatory effect of metformin is repressed by a specific ATM kinase inhibitor KU-55933[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | ATM for use in the in vitro assay is obtained by immunoprecipitation with rabbit polyclonal antiserum raised to the COOH-terminal 400 amino acids of ATM in buffer containing 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 2 mM MgCl2, 250 mM KCl, 500 μM EDTA, 100 μM Na3VO4, 10% v/v glycerol, and 0.1% v/v Igepal. ATM-antibody complexes are isolated from nuclear extract by incubating with protein A-Sepharose beads for 1 hour and then through centrifugation to recover the beads. In the well of a 96-well plate, ATM-containing Sepharose beads are incubated with 1 μg of substrate glutathione S-transferase-p53N66 (NH2-terminal 66 amino acids of p53 fused to glutathione S-transferase) in ATM assay buffer [25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 75 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 50 μM Na3VO4, 500 μM DTT, and 5% v/v glycerol] at 37°C in the presence or absence of inhibitor. After 10 minutes with gentle shaking, ATP is added to a final concentration of 50 μM and the reaction continued at 37°C for an additional 1 hour. The plate is centrifuged at 250×g for 10 minutes (4°C) to remove the ATM-containing beads, and the supernatant is removed and transferred to a white opaque 96-well plate and incubated at room temperature for 1.5 hours to allow glutathione S-transferase-p53N66 binding. This plate is then washed with PBS, blotted dry, and analyzed by a standard ELISA technique with a phospho-serine 15 p53 antibody. The detection of phosphorylated glutathione S-transferase-p53N66 substrate is performed in combination with a goat antimouse horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody. Enhanced chemiluminescence solutionis used to produce a signal and chemiluminescent detection is carried out via a TopCount plate reader. |
| Cell Assay | 1BR or AT4 cells are seeded in 10-cm Petri dishes and treated on day 2 (80 to 90% confluence). Cells are preincubated for 1 hour with KU-55933 or vehicle control and then exposed to 5 Gy of ionizing radiation. Time courses of cell cycle distribution are performed, and the optimal time for discrimination of populations is selected as 16 hours. All subsequent experiments are performed at the 16-hour time point. Cells are stained with propidium iodide according to standard protocols and analyzed by FACS with a FACScalibur. Exponentially growing (50-70% confluent) SW620 cells in 60 mm dishes are exposed to KU-55933 or DMSO for 1 h before addition of etoposide (final concentration of 0.1 and 1 μM) for 16 h before harvesting, propidium iodide staining and analysis as above. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 628.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 229.98° C |
| Molecular Formula | C21H17NO3S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 395.495 |
| Flash Point | 333.6±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 395.064972 |
| PSA | 93.28000 |
| LogP | 6.13 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.714 |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at -20°C |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
~62% 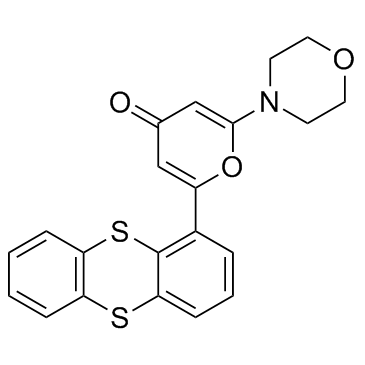
587871-26-9 |
| Literature: Hollick, Jonathan J.; Rigoreau, Laurent J. M.; Cano-Soumillac, Celine; Cockcroft, Xiaoling; Curtin, Nicola J.; Frigerio, Mark; Golding, Bernard T.; Guiard, Sophie; Hardcastle, Ian R.; Hickson, Ian; Hummersone, Marc G.; Menear, Keith A.; Martin, Niall M. B.; Matthews, Ian; Newell, David R.; Ord, Rachel; Richardson, Caroline J.; Smith, Graeme C. M.; Griffin, Roger J. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2007 , vol. 50, # 8 p. 1958 - 1972 |
|
~% 
587871-26-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 50, # 8 p. 1958 - 1972 |
|
~% 
587871-26-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 50, # 8 p. 1958 - 1972 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |