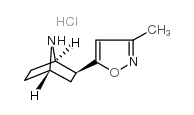
188895-96-7
| Name | 5-[(1S,3S,4R)-7-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-3-yl]-3-methyl-1,2-oxazole |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
7-Azabicyclo(2.2.1)heptane,2-(3-methyl-5-isoxazolyl)-,exo
(+-)-Epiboxidine exo-2-(3-Methyl-5-isoxazolyl)-7-azabicyclo(2.2.1)heptane |
| Description | Epiboxidine is a potent and selective neural nAChR agonist with Kis of 0.46 nM and 1.2 nM for rat and human α4β2 nAChRs, respectively. Epiboxidine is a methylisoxazole analog of the alkaloid Epibatidine, and is also an analog of another nAChR agonist, ABT 418[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 0.46 nM (rat α4β2 nAChR) and 1.2 nM (human α4β2 nAChR)[1] |
| In Vitro | Epiboxidine has affinity and functional at central neuronal α4β2 receptors, with Kis of 0.46 and 1.2 in rat and humen[1]. Epiboxidine has activity at ganglionic-type α3β4*-nicotinic receptors of PC12 cells, with a Ki of 19[1]. Epiboxidine is much less toxic than Epibatidine[1]. Epiboxidine stimulates sodium-22 influx in PC12 and TE671 cells, with EC50s of 0.18 and 2.6 µM[2]. |
| In Vivo | Epiboxidine (20 μg/kg; ip; once) treatment shows marked analgetic activity in mice[1]. Epiboxidine (50 and 100 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injected; once) causes marked antinociception as measured in the hot-plate assay[2]. Epiboxidine inhibits [3H]nicotine binding in rat cerebral cortical membranes, with a Ki of 0.6 nM[2]. Animal Model: Adult male NIH Swiss strain mice (25-30 g)[2] Dosage: 50 and 100 mg/kg Administration: I.p.; once Result: Caused a dose-related Straub tail, hypomotility, hypoventilation and piloerection. |
| References |
| Density | 1.13g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 313.1ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C10H14N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 178.23 |
| Flash Point | 143.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 214.08700 |
| PSA | 38.06000 |
| LogP | 2.72170 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.000507mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.53 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CL5446415 |