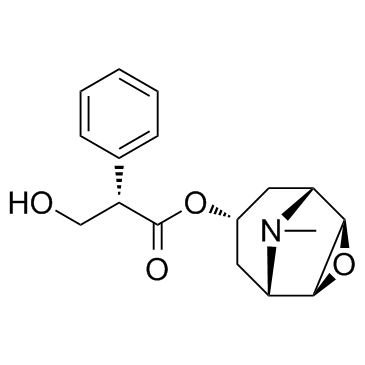
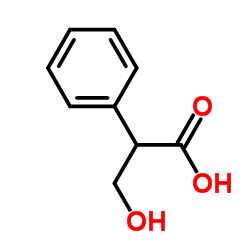
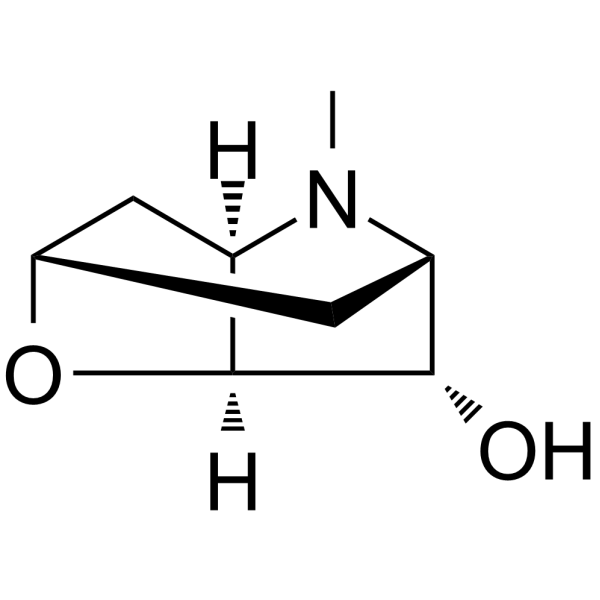
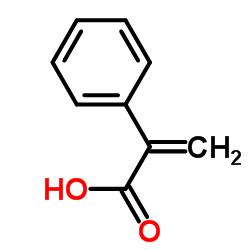
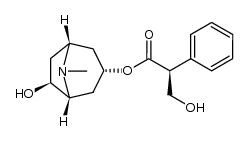
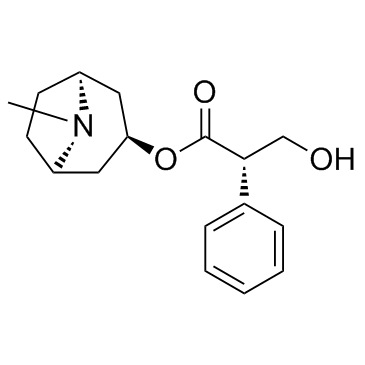
51-34-3
| Name | scopolamine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
l-Scopolamine
Atrochin Transderm-V Tropic Acid Ester with Scopine TRANSDERM SCOP Transcop Skopolate 6b,7b-Epoxy-3a-tropanyl S-(-)-Tropate scopadulcic acid B Skopyl 1-METHYL-3-NONYLIMIDAZOLIUM BROMIDE, 99% SCOP (1R,2R,4S,5S,7s)-9-Methyl-3-oxa-9-azatricyclo[3.3.1.0]non-7-yl (2S)-3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate Atroscine [7(S)-(1a,2b,4b,5a,7b)]-a-(Hydroxymethyl)benzeneacetic Acid 9-Methyl-3-oxa-9-azatricyclo[3.3.1.02,4]non-7-yl Ester (-)-Scopolamine ATROQUIN scopolamine 6β,7β-Epoxy-3α-tropanyl S-(-)-tropate UNII-DL48G20X8X Scopoderm TTS 6b,7b-Epoxy-1aH,5aH-tropan-3a-ol (-)-Tropate Scopoderm (−)-Scopolamine Scopine tropate EINECS 200-090-3 |
| Description | Scopolamine is a high affinity (nM) muscarinic antagonist. 5-HT3 receptor-responses are reversibly inhibited by Scopolamine with an IC50 of 2.09 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
5-HT3 Receptor:2.09 μM (IC50) mAChR |
| In Vitro | Application of Scopolamine to oocytes expressing 5-HT3 receptors does not elicit a response when applied alone, but causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of the response during a co-application of 2 μM 5-HT. The pIC50 value for Scopolamine is 5.68±0.05 (IC50=2.09 μM, n=6) with a Hill Slope of 1.06 ± 0.05. This gave a Kb of 3.23 μM. The same concentration-dependent effect is also seen when Scopolamine is applied during the 5-HT application. To further test for a competitive binding at the 5-HT3 receptor, the competition of unlabelled Scopolamine is measured with [3H]granisetron, an established high-affinity competitive antagonist at these receptors. Scopolamine displays concentration-dependent competition with 0.6 nM [3H]granisetron (~Kd), yielding an average pKi of 5.17±0.24 (Ki=6.76 μM, n=3)[1]. |
| In Vivo | In the histopathology study, there is no significant change in the histology of the brain. However, it is observed that there is a reduction in density of cells in the hippocampus of the control mice pretreated with Scopolamine who received only distilled water[2]. Scopolamine administration alone significantly increases the activity of Acetylcholinesterase enzyme (AchE) (7.98±0.065; P<0.001) when compared to the normal group (3.06±0.296). The animals treated with Scopolamine report a significant increase (34.61±4.85; P<0.01) in levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) as compared to the normal group (12.82±2.86). The Scopolamine-treated group shows significant decrease in reduced glutathione (GSH) level (P<0.001; 0.1504±0.03) as compared to the normal group (0.3906±0.02). The Scopolamine-treated rats show a significant increase in the concentration ofβ amyloid (Aβ1-42) (P<0.001; 146.2±1.74) as compared to the normal group (43.21±3.46)[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Saturation binding (8 point) curves are measured by incubating either crude extracts of HEK 293 cells stably expressing 5-HT3 receptors, or Guinea pig membrane preparations, in 0.5 mL incubations containing 10 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.4) and 0.1-1 nM [3H]granisetron or 1-10 nM [3H]N-methylScopolamine. Competition binding (10 point) is determined by incubating the same receptors preparations in 0.5 mL HEPES buffer containing either 0.6 nM [3H]granisetron or 0.6 nM [3H]N-methylScopolamine, and differing concentrations of competing ligands. Non-specific binding is determined with 1 mM quipazine or 10 μM Scopolamine respectively. Incubations are terminated by filtration onto Whatman GF/B filters wetted with HEPES buffer+0.3% polyethyleneimine, followed by two rapid washes with ice-cold HEPES buffer. Protein concentration is calculated using a Lowry protein assay with bovine serum albumin standards. Radioactivity is measured using a Tri-Carb 2100 TR scintillation counter[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] The mice are weighed, labeled and grouped into seven groups of 5 animals each after which all animals are pre-injected intraperitoneally with 3 mg/kg Scopolamine. Groups 1-3 are administered 0.2 mL equivalent doses of 4 mg/kg, 6 mg/kg and 8 mg/kg of the extract of Morinda lucida while groups 4-6 are given same doses of Peltophorum pterocarpum extract and group 7 is given 0.2 mL of distilled water (negative control) for 3 consecutive days. Rats[3] Healthy male Wistar rats (12 months old) weighing 180–200 g are used in this study. Rats are divided into five groups (n=6/group); Group I-normal control, Group II-disease control (Scopolamine hydrobromide 3 mg/kg, i.p.), Group III-Scopolamine+Quercetin (25 mg/kg, p.o.), Group IV-standard treatment (Scopolamine+Donepezil hydrochloride 3 mg/kg, p.o.), and Group V-Scopolamine+Quercetin (25 mg/kg, p.o.)+Donepezil (3 mg/kg, p.o.). Group III, IV, and V rats are dosed every 24 h interval with respective drugs for 14 consecutive days. The acquisition trail for Morris water maze, elevated plus maze, and passive avoidance paradigm is carried out on the 14th day, and Scopolamine (3 mg/kg, i.p.) is administered on the 14th day after the acquisition trail to all groups except normal control group, which provoke the cognitive impairment in rats. Retention of memory is tested on the 15th day, and on the same day, rats are sacrificed and brain tissues are isolated to estimate acetylcholinesterase enzyme (AchE) and brain oxidative stress markers such as lipid peroxidase (LPO), glutathione (GSH) (reduced). ELISA kit is used to estimate β amyloid (Aβ1-42) level. The hippocampus of rat brains is dissected out and studied for histopathological changes. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 460.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 59ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C17H21NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 303.353 |
| Flash Point | 232.2±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 303.147064 |
| PSA | 62.30000 |
| LogP | 0.76 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.614 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |