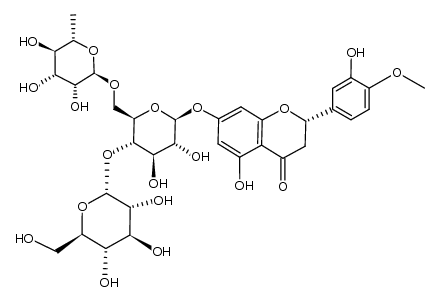
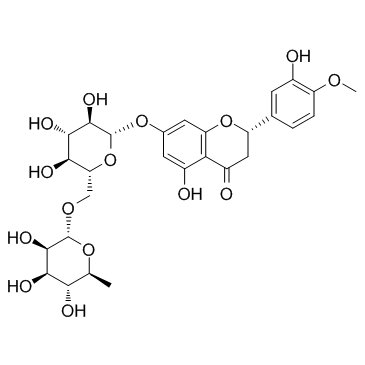
520-26-3
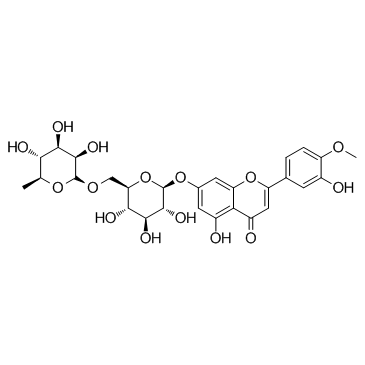
| Name | hesperidin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
usafcf-3
Hesperetin 7-rhamnoglucoside,Hesperitin-7-rutinoside VITAMIN P Hespeidin Hespiridin Hesperiden Neobiletin cirantin MFCD00075663 Hesperetin7-rutinoside Cirontin Hesperidoside Hesperetin7-rhamnoglucoside Hesperidin EINECS 208-288-1 |
| Description | Hesperidin (HP) is a bioflavonoid that plays a role in plant defense and is abundant in citrus species, such as grapefruit, lemon and orange. Hesperidin is used effectively as a supplemental agent in complementary therapy protocols, since it possesses biological and pharmacological properties as an effective antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic, and anti-hypertensive agent with lipid-lowering activity[1]IC50: hesperidin (IC50=116.68μmo/L))[4]in vitro: hesperidin and linarin are two of the main constituent of Valeriana's extract exhibiting a high affinity to KATP channel, which are related to the control of Ca++ concentration and release of GABA in synaptic nerve terminal, mainly on cells of SN[2]in vivo: Hesperidin was dissolved in 1% carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and administered orally at a dose of 50 mg/kg for 10 consecutive days. In the control group, rats were treated with the corn oil and 1% CMC vehicle.[1] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 930.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 250-255 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C28H34O15 |
| Molecular Weight | 610.561 |
| Flash Point | 305.5±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 610.189758 |
| PSA | 234.29000 |
| LogP | 1.78 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.695 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MK6650000 |
|
~% 
520-26-3 |
| Literature: Yamada, Mika; Tanabe, Fujimi; Arai, Norie; Mitsuzumi, Hitoshi; Miwa, Yoshikatsu; Kubota, Michio; Chaen, Hiroto; Kibata, Masayoshi Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 2006 , vol. 70, # 6 p. 1386 - 1394 |
|
~% 
520-26-3 |
| Literature: Yamada, Mika; Tanabe, Fujimi; Arai, Norie; Mitsuzumi, Hitoshi; Miwa, Yoshikatsu; Kubota, Michio; Chaen, Hiroto; Kibata, Masayoshi Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 2006 , vol. 70, # 6 p. 1386 - 1394 |
|
~% 
520-26-3 |
| Literature: Shimokoriyama Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1957 , vol. 79, p. 4199,4200 |
|
~% 
520-26-3 |
| Literature: Belboukhari, Nasser; Cheriti, Abdelkrim; Roussel, Christian; Vanthuyne, Nicolas Natural Product Research, 2010 , vol. 24, # 7 p. 669 - 681 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 6 | |