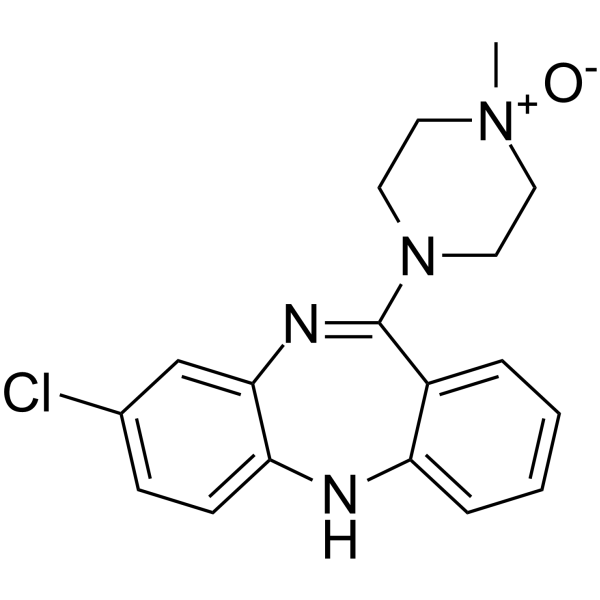
34233-69-7
| Name | clozapine n-oxide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
8-Chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo[b,e](1,4)diazepine N-oxide
8-Chloro-11-(4-methyl-4-oxido-1-piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepine 5H-Dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepine, 8-chloro-11-(4-methyl-4-oxido-1-piperazinyl)- Clozapine N-oxide Clozapine (N-oxide) |
| Description | Clozapine N-oxide (CNO) is a major metabolite of the anti-psychotic drug clozapine. Clozapine N-oxide is a agonist for the chemogenetic Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drug (DREADD) system. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
DREADD[1] |
| In Vivo | After a single intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of Clozapine N-oxide (1 mg/kg) into mice, Clozapine N-oxide (CNO) plasma levels peak at 15 min and are very low after 2 h. Acutely administered CNO can be metabolically converted to Clozapine in other species such as human and guinea-pig. The metabolites that may form after chronic administration of CNO to DREADD-expressing mice (or other species) have not been studied systematically. However, even if back-transformation to Clozapine occurs after chronic CNO administration, it should be noted that Clozapine is a more potent (by ~10-fold) DREADD agonist than CNO itself. Moreover, confounding biological effects of potential CNO metabolites can be easily identified by including both saline- and CNO-treated WT animals in a particular DREADD study. Despite the short plasma half-life of CNO in mice, the biological effects that have been described after acute treatment of DREADD-expressing experimental animals are usually much longer (6-10 h). One possibility is that CNO tends to accumulate in tissues, although other scenarios are also feasible[1]. Using a general pharmacokinetic model for the interconversion process, the mean total clearances of Clozapine and Clozapine N-oxide (CNO) are 28.45 L/hr and 45.30 L/hr, respectively[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.36g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 517.4ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 190-248ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C18H19ClN4O |
| Molecular Weight | 342.823 |
| Flash Point | 266.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 342.124725 |
| PSA | 57.06000 |
| LogP | 0.76 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.685 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | 22-36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| RTECS | HP1760000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |