739-71-9
| Name | trimipramine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(+-)-1-cyclohexyl-1-phenyl-3-piperidino-propan-1-ol,hydrochloride
(+-)-1-Cyclohexyl-1-phenyl-3-piperidino-propan-1-ol,Hydrochlorid tremin (+/-)-Trihexyphenidyl hydrochloride EINECS 212-008-3 Trihexy 5-(3-dimethylamino-2-methylpropyl)-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz (b,f) azepine acid maleate triiodothyronine Trimipramine paralest 8-Chloro-3-methoxy-11-(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[5,6]-cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-ol [3-(10,11-dihydro-dibenzo[b,f]azepin-5-yl)-2-methyl-propyl]-dimethyl-amine 10,11-dihydro-5-(3-dimethylamino-2-methylpropyl)-5H-dibenz(b,f)azepine peragit Sedrina timipramine cyclodol trihexylphenidyl HCl pacitane Broflex 3,3',5-triiodothyronine L-3,3',5-triiodothyronine 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine pipanol |
| Description | Trimipramine is a 5-HT receptor antagonist, with pKi binding values of 6.39, 8.10, 4.66 for 5-HT1C, 5-HT2 and 5-HT1A, respectively. Trimipramine is also a potent and selective inhibitor targeting human noradrenaline (hNAT), serotonin (hSERT) and organic cation transporters (hOCT1, hOCT2) with IC50 values of 4.99 μM, 2.11 μM, 3.72 μM, 8.00 μM, respectively. Trimipramine has vascular activity and anxiolytic efficacy[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
5-HT1C Receptor:6.39 (pKi) 5-HT2 Receptor:8.10 (pKi) 5-HT1A Receptor:4.66 (pKi) |
| In Vitro | Trimipramine displays much higher affinity for 5-HT2 than for 5-HT1C receptors[1]. Trimipramine is a moderate inhibitor of the human NAT and SERT, with the IC50 values of 4.99 μM and 2.11 μM, respectively[2]. SERT and NAT could represent a target for the antidepressant effects of trimipramine (1 mM, 0.1 mM, 0.01 mM, 1 μM, 0.1 μM; 10 min; HEK293 cells)[2]. |
| In Vivo | Trimipramine (5 mg/kg/d; 14 d; chronic administration) acts as functions in rats:1. Increasing concentration of regional 5-HT. 5-HT is highest in the frontal cortex and the hippocampus, followed by the olfactory tubercles and the hypothalamus. 2. Decreasing the number of frontal cortex 5-HT2 and striatal DA D2 receptors. 3. Increasing in the brain regional level of monoamines and metabolites. thus indicates a greater synthesis rate for dopamine (DA) and 5-HT coinciding with an adaptive down regulation of 5-HT2 and DA D2 receptors[3]. Animal Model: Male Wistar rats (220-250 g); implanted osmotic minipump subcutaneously in the dorsal thoracic interscapular region[3] Dosage: 5 mg/kg/day Administration: Delivered by smotic minipump; 14 days Result: Decreased the number of frontal cortex 5-HT2 and striatal DA D2 receptors, thus blocked the uptake of 5-HT and dopamine (DA). |
| References |
| Density | 0.9912 (rough estimate) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 426.2°C (rough estimate) |
| Melting Point | 45° |
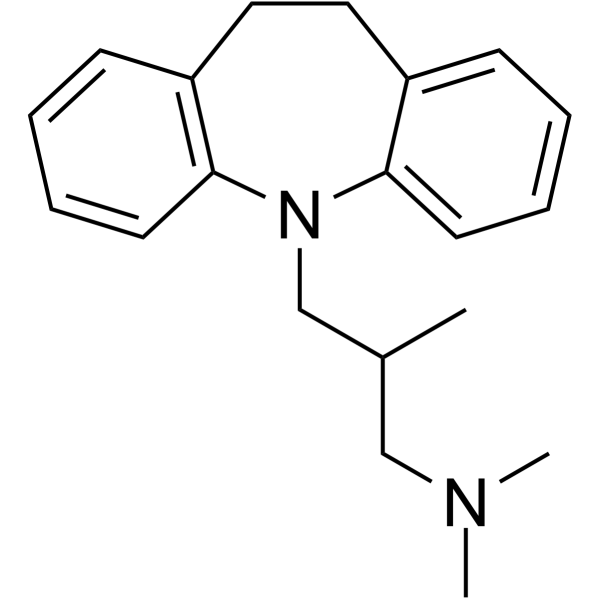
| Molecular Formula | C20H26N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 294.43400 |
| Flash Point | 9℃ |
| Exact Mass | 294.21000 |
| PSA | 6.48000 |
| LogP | 4.18600 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.6450 (estimate) |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H301 + H311 + H331-H370 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P260-P280-P301 + P310-P311 |
| Hazard Codes | F,T |
| Risk Phrases | 11-23/24/25-39/23/24/25 |
| Safety Phrases | 16-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 3249 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |