| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
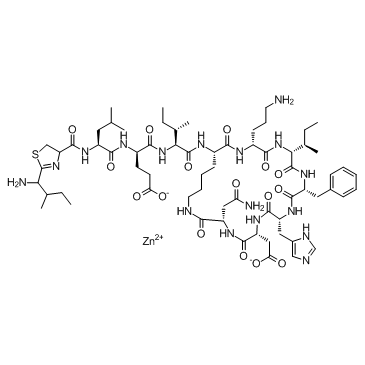 |
Bacitracin zinc
CAS:1405-89-6 |
|
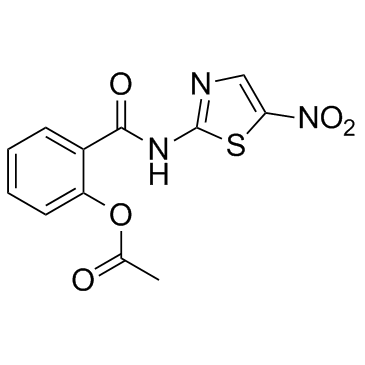 |
Nitazoxanide
CAS:55981-09-4 |
|
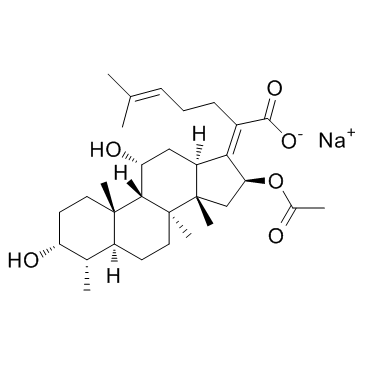 |
Fusidic acid (sodium salt)
CAS:751-94-0 |
|
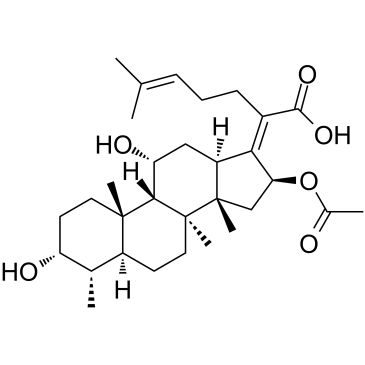 |
fusidic acid
CAS:6990-06-3 |
|
 |
Bacitracin
CAS:1405-87-4 |
|
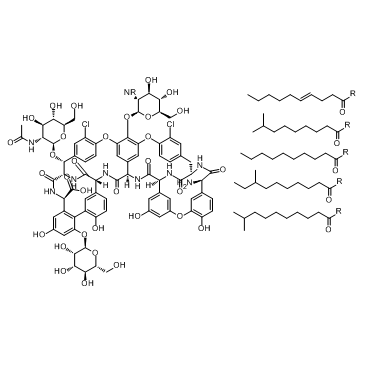 |
Teicoplanin
CAS:61036-62-2 |