Teicoplanin
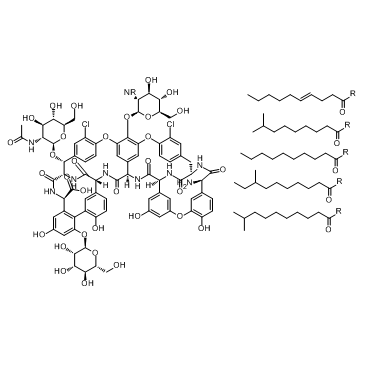
Teicoplanin structure
|
Common Name | Teicoplanin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 61036-62-2 | Molecular Weight | 2526.73 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C130H175Cl2N9O37R6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Role of extra-cellular fatty acids in vancomycin induced biofilm formation by vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 26(2) , 383-9, (2013) In the present study a vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) (VRSA) (Labeled as CP2) was isolated from the blood of a post-operative cardiac patient is described. It harbors a plasmid which carry vanA gene and exhibited low-level vancomycin r... |
|
|
A screen of approved drugs and molecular probes identifies therapeutics with anti-Ebola virus activity.
Sci. Transl. Med. 7 , 290ra89, (2015) Currently, no approved therapeutics exist to treat or prevent infections induced by Ebola viruses, and recent events have demonstrated an urgent need for rapid discovery of new treatments. Repurposing approved drugs for emerging infections remains a critical ... |
|
|
Once-weekly dalbavancin versus daily conventional therapy for skin infection.
N. Engl. J. Med. 370(23) , 2169-79, (2014) Dalbavancin, a lipoglycopeptide antibiotic agent that is active against gram-positive pathogens, has a long plasma half-life, allowing for once-weekly dosing. DISCOVER 1 and DISCOVER 2 were identically designed noninferiority trials of dalbavancin for the tre... |
|
|
Pharmacology and the treatment of complicated skin and skin-structure infections.
N. Engl. J. Med. 370(23) , 2238-9, (2014) Skin and skin-structure infections are estimated to cause more than 15 million infections1 and 870,000 hospital admissions2 annually in the United States. Rates of these infections are substantially higher than they were 10 to 20 years ago, owing in part to t... |
|
|
Synthesis of isoindole and benzoisoindole derivatives of teicoplanin pseudoaglycon with remarkable antibacterial and antiviral activities.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22(23) , 7092-6, (2012) The primary amino function of teicoplanin pseudoaglycon has been transformed into arylthioisoindole or benzoisoindole and glycosylthioisoindole derivatives, in a reaction with o-phthalaldehyde or naphtalene-2,3-dicarbaldehyde and various thiols. All of the ob... |
|
|
DrugBank 3.0: a comprehensive resource for 'omics' research on drugs.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39 , D1035-41., (2011) DrugBank (http://www.drugbank.ca) is a richly annotated database of drug and drug target information. It contains extensive data on the nomenclature, ontology, chemistry, structure, function, action, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, metabolism and pharmaceutic... |
|
|
The effect of low dose teicoplanin-loaded acrylic bone cement on biocompatibility of bone cement.
Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 60(2) , 117-25, (2013) Antibiotic-loaded acrylic bone cement (polymethylmethacrylate, PMMA) is used to prevent or treat infection in total joint replacement surgery. The purpose of this study was to investigate biocompatibility and cytotoxicity of the teicoplanin-loaded acrylic bon... |
|
|
Current state of Clostridium difficile treatment options.
Clin. Infect. Dis. 55 Suppl 2 , S71-6, (2012) Recent reports of reduced response to standard therapies for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) and the risk for recurrent CDI that is common with all currently available treatment agents have posed a significant challenge to clinicians. Current recommenda... |
|
|
Update of dalbavancin spectrum and potency in the USA: report from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (2011).
Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 75(3) , 304-7, (2013) Dalbavancin (DAL) is an investigational lipoglycopeptide with a prolonged serum half-life allowing once weekly dosing. DAL potency was assessed in the 2011 SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program among 1555 isolates sampled from all 9 US Census regions. Mon... |
|
|
Linezolid versus vancomycin or teicoplanin for nosocomial pneumonia: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.
Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 32(9) , 1121-8, (2013) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is an important cause of nosocomial pneumonia. Compared with glycopeptide antibiotics, linezolid achieves higher lung epithelial lining fluid concentrations, which may have an advantage in treating nosocomial... |