| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Polymyxin B Sulfate
CAS:1405-20-5 |
|
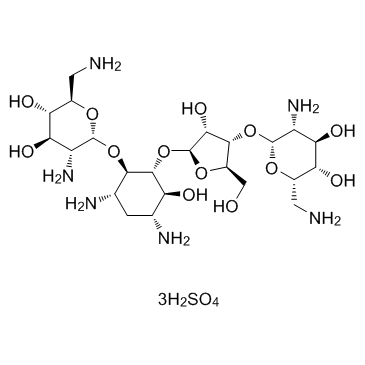 |
Neomycin sulfate
CAS:1405-10-3 |
|
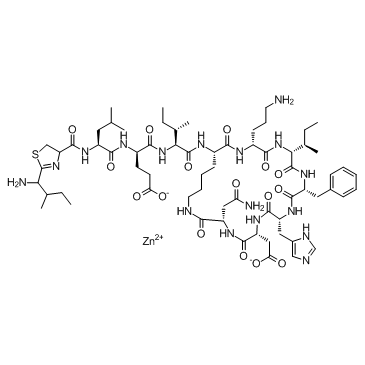 |
Bacitracin zinc
CAS:1405-89-6 |
|
 |
Bacitracin
CAS:1405-87-4 |