| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
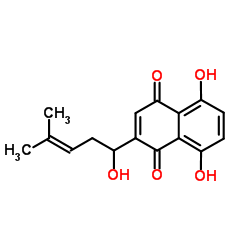 |
Shikonin
CAS:54952-43-1 |
|
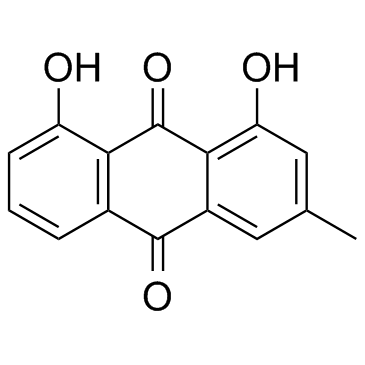 |
Chrysophanic acid
CAS:481-74-3 |
|
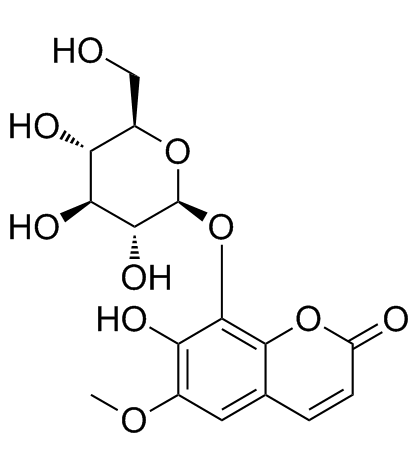 |
Fraxin
CAS:524-30-1 |