Inhibitory effect of Shikonin on Candida albicans growth.
Hao Miao, LiuYa Zhao, ChunLi Li, QingHua Shang, Hui Lu, ZiJin Fu, Li Wang, YuanYing Jiang, YingYing Cao
Index: Biol. Pharm. Bull. 35(11) , 1956-63, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Our study showed that Shikonin (SK) could provide an action against almost all Candida albicans isolates tested. More importantly, to some Fluconazole (FCZ)-resistant Candida albicans, the action of SK (MIC(80) value 4 µg/mL) was shown to be >16 times higher than that of FCZ (MIC(80) >64 µg/mL). To clarify the mechanism underlying this action, we performed a comparative study in untreated control C. albicans and C. albicans treated with SK. In this study, we found that SK treatment increased generation of endogenous reactive oxygen species (ROS) and decreased mitochondrial membrane potential. Furthermore, anti-oxidants N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and glutathione (GSH) could reduce the antifungal activity of SK significantly in C. albicans. Our analyses also identified 9 differentially expressed genes, which were related to glycolysis-related genes (CDC19 and HXK2), fermentation-related genes (ALD5 and ADH1), antioxidant defense-related genes (SOD2 and SOD5), thioredoxin reductase-related gene (TRR1), mitochondrial respiratory electron transport chain-related gene (MRF1) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidoreductase-related gene (EBP1). These results suggest that mitochondrial aerobic respiration shift and endogenous ROS augmentation contribute to the action of SK against C. albicans.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
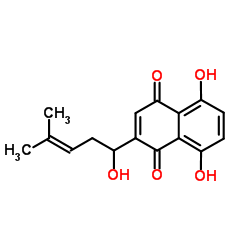 |
Shikonin
CAS:54952-43-1 |
C16H16O5 |
|
Screening for novel quorum-sensing inhibitors to interfere w...
2011-12-01 [J. Med. Microbiol. 60(Pt 12) , 1827-34, (2011)] |
|
Optimization of shikonin homogenate extraction from Arnebia ...
2013-01-01 [Molecules 18(1) , 466-81, (2013)] |
|
Glutathione-S-transferase enhances proliferation-migration a...
2011-11-01 [Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 27(11) , 477-84, (2011)] |
|
Ionization of shikonin derivatives using negative-ion electr...
2012-05-01 [J. Mass Spectrom. 47(5) , 581-5, (2012)] |
|
Chemical inducers of heat shock proteins derived from medici...
2012-01-01 [Int. J. Hyperthermia 28(1) , 1-8, (2012)] |